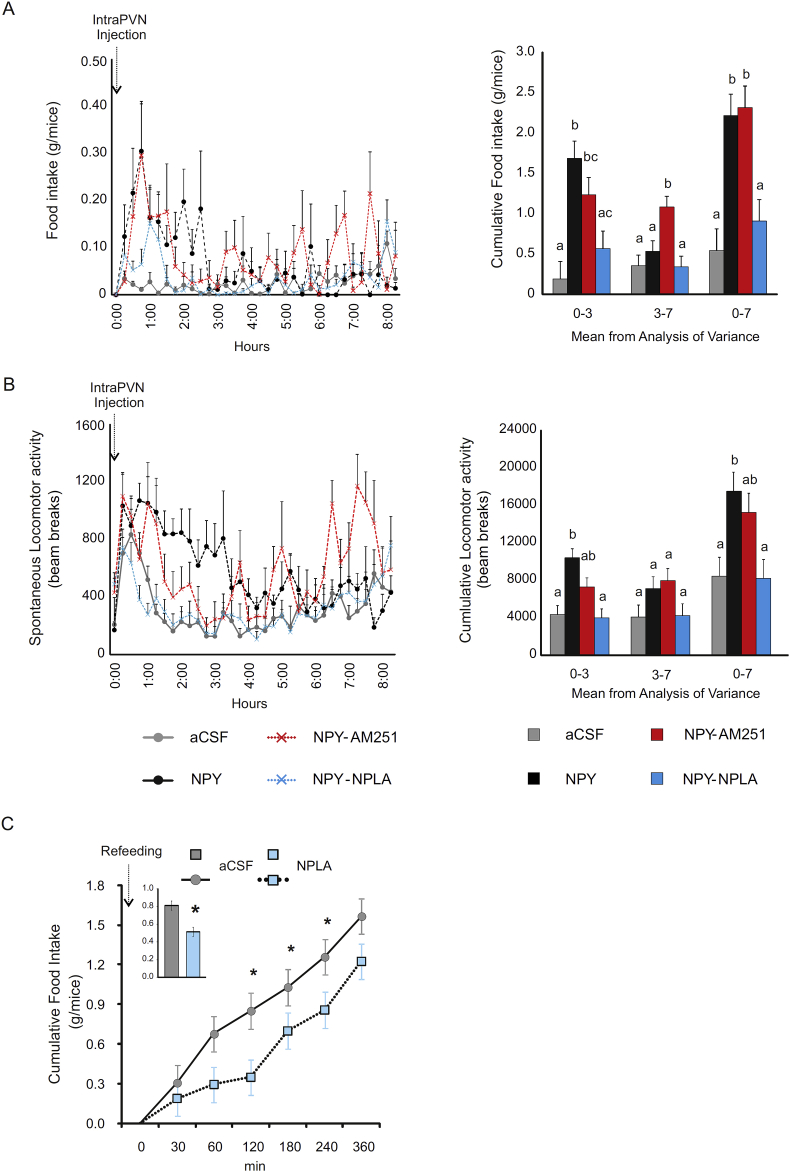
Figure 6.
Effect of intraPVN co-administration of NPY with the CB1 antagonist, AM251, or the nNOS inhibitor, NPLA, on food intake and locomotor activity. Food intake (A) and spontaneous activity (B) of mice injected intraPVN with CSF (grey), NPY alone (black) and NPY co-administrated with AM251 (red) or NPLA (blue). (See also in Supplementary Figure 7) Food intake and spontaneous locomotor activity was monitored over 8 h post injection. The cumulative graph is presented in Supplementary Figure 7. While AM251 did not influenced the cumulative food intake of NPY treated mice, NPLA prevented the NPY induced increase of food intake (A). Similarly, AM251 had only minor effect on the locomotor activity, while NPLA completely prevented the NPY induced increase of the locomotor activity in the presence of food (B). IntraPVN injection of NPLA alone (light blue) diminished food intake following an overnight fast (C). Mean ± SEM extracted from the analysis of variance of food intake and spontaneous locomotor activity are represented in the bar graphs. Data with different superscripts letters are significantly different (P < 0.05) according to the ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. n = 8 mice per group.