Figure 1.
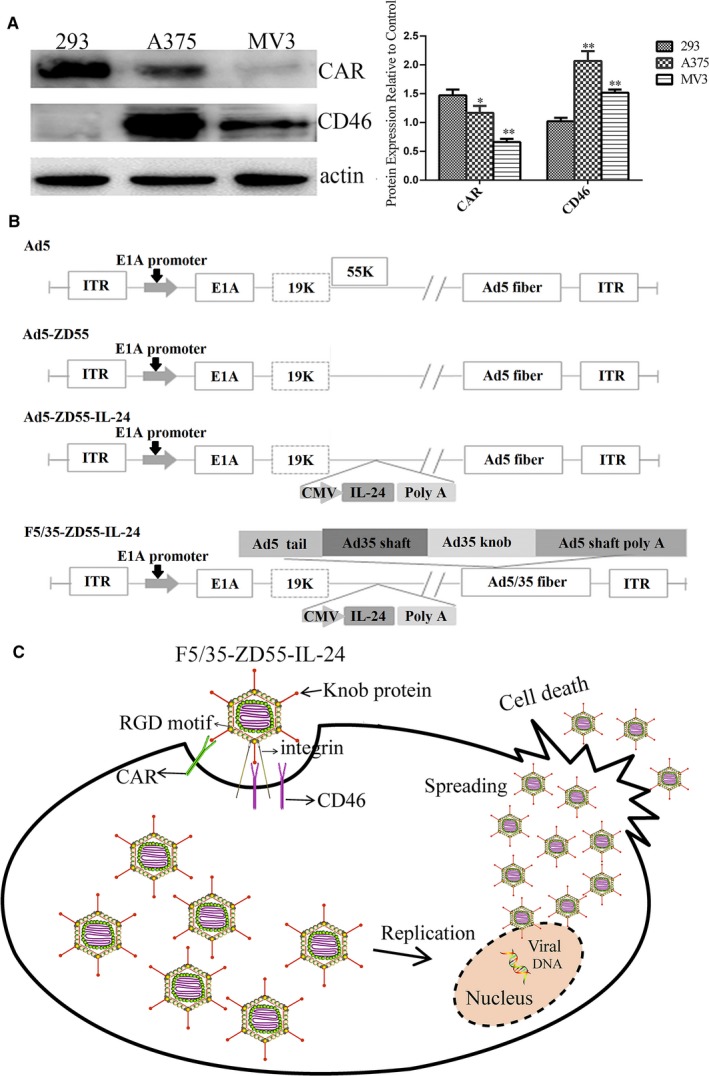
The expression levels of CAR and CD46 in melanoma cells and schematic diagrams of the adenovirus vectors and the mechanism of the novel chimeric adenovirus. A, Western blotting was performed to measure expression levels of CAR and CD46. β‐actin was used as a loading control. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 vs 293 cells. B, Ad5, Ad5‐ZD55, Ad5‐ZD55‐IL‐24, and F5/35‐ZD55‐IL‐24. Ad5‐ZD55 includes an E1B‐55 K deletion. F5/35 fiber: 5 and 35 type adenoviral chimeric fiber. ITR: inverted terminal repeats. Ad5‐ZD55‐EGFP and F5/35‐ZD55‐EGFP (not shown) have the same structure as Ad5‐ZD55‐IL‐24 or F5/35‐ZD55‐IL‐24, with IL‐24 replaced by EGFP. C, F5/35‐ZD55‐IL‐24 firstly attaches to cells via CD46 or CAR. Once attached, the RGD motif in the penton base interacts with integrin, promoting endocytosis, and internalization of the adenovirus. The tumor cells are then lysed by F5/35‐ZD55‐IL‐24 via apoptosis. The released adenovirus infects adjacent tumor cells. CAR, coxsackie‐adenovirus receptor
