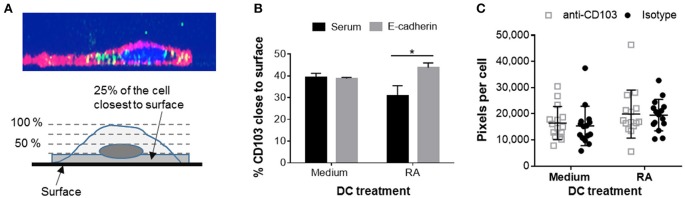
Figure 6.
Adhesion of RA-treated MoDCs to E-cadherin-coated surfaces alters distribution of CD103. DC interactions with E-cadherin were analyzed by performing adhesion and spreading assays on glass slides coated with recombinant human E-cadherin. (A,B) RA-treated and untreated MoDCs were added to E-cadherin-coated slides and were incubated at 37°C for 40 min. Cells were then fixed, permeabilized and stained for CD103 expression. Z-stack images (0.5 μm step size) of adherent MoDCs were collected by confocal microscopy and analyzed for the distribution of CD103 in relation to the glass surface. (A) Top panel: orthogonal representation of an immunofluorescently labeled MoDC adhered to a glass surface and analyzed by z-stack confocal imaging. CD11c: red, CD103: green, DAPI nuclear stain: blue. Bottom panel: graphical representation of the image analysis approach. (B) Summarized data from three independent experiments were analyzed. *P ≤ 0.05, 1-way ANOVA with Tukey's post-hoc test. (C) Spreading analysis of DCs on E-cadherin-coated glass slides. Glass slides were first coated with anti-human IgG antibodies and then with recombinant human E-cadherin-Fc. MoDCs generated in the presence of medium alone or 100 nM RA were pre-treated with a CD103 neutralizing antibody or an isotype control antibody for 30 min at 4°C. Cells were then added to the slides in the presence of 2 mM Mn2+ and incubated at 37°C for 40 min. Cell spreading was analyzed by fluorescence microscopy based on HLA-DR+ pixels per nucleus. Individual data points (n = 15 areas), mean and SEM from one representative out of 3 independent experiments are shown.