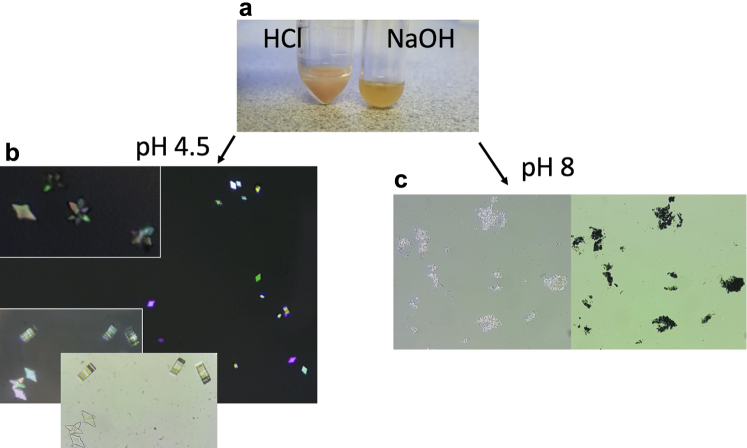
Figure 3.
The effect of pH on uric acid crystallization. One drop of 1 N HCl solution (1 normal = 36.5 g hydrochloric acid/1 liter) was mixed with 2 ml of patient’s urine resulting in a reduction of pH, pinkish hue (a, left test tube) on gross inspection, and polychromatic birefringence uric acid crystallization with light microscopy (b). In a similar fashion, 1 drop of 1 N NaOH solution (1 N = 40 g sodium hydroxide/1 liter) was mixed with 2 ml of urine to serve as a negative-treatment response control. On NaOH addition, urine color became a dirty yellow (a, right test tube), urine pH increased, and amorphous crystals were present when analyzed with light microscopy (c).