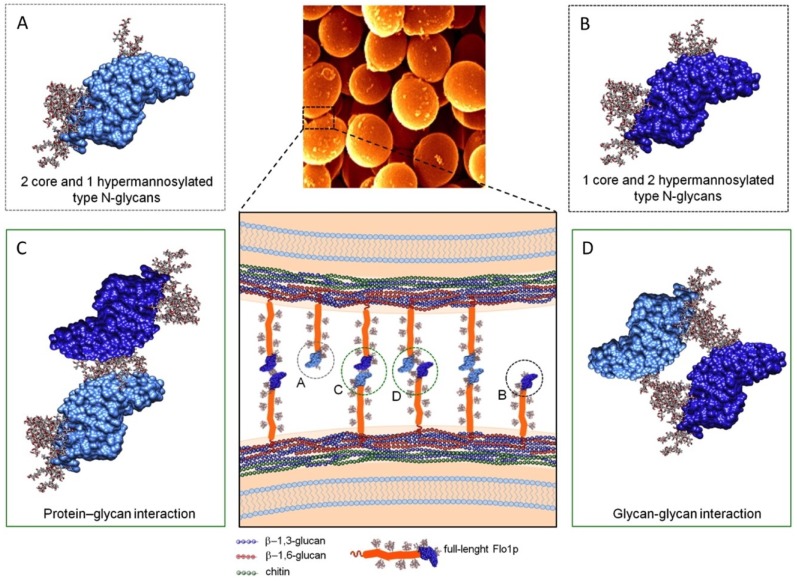
Figure 7.
Molecular flocculation model based on Flo1p homophilic self-interaction. The two populations of N-Flo1p, which carry different types of N-glycans, are illustrated. Two S. cerevisiae cells bind together via Flo1p self-interaction. This binding is accomplished via lectin-glycan and glycan-glycan interactions. (A) 36 kDa of N-Flo1p containing two short core type N-glycans (Man8-14GlcNAc oligosaccharides) and one large hyperglycosylated type N-glycans (Man>50GlcNAc). (B) 100 kDa of N-Flo1p containing one short core type and two large hypermannosylated type N-glycans. (C) Lectin–protein interaction. (D) Glycan-glycan interaction. Reprinted from [39].