Figure 1.
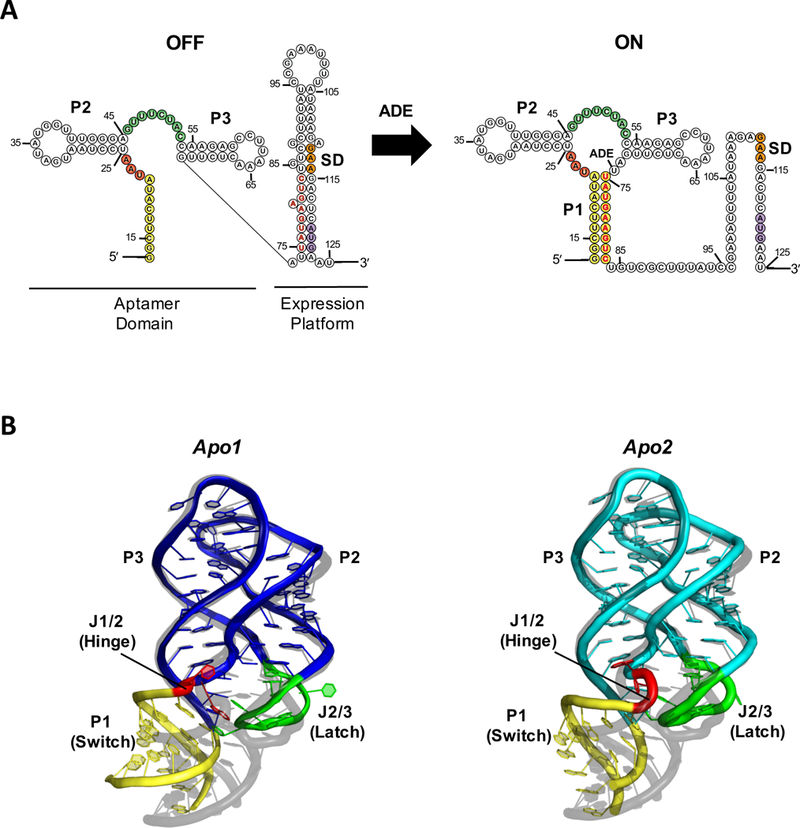
(A) Secondary structure of the V. vulnificus add adenine riboswitch and (B) Crystal structure of the ligand-free aptamer domain in apo1 (left, blue) and apo2 (right, cyan) states (PDB:5E54), aligned to the ligand-bound structure (grey, PDB:4TZX) for comparison. The P1 helix (yellow), J1/2 hinge (red), and J2/3 latch (green) regions, which exhibit the greatest structural differences among rA71 conformational states, are highlighted. The switching sequence is denoted in red bold letters, the Shine-Dalgarno in orange, and the start codon in purple. The sequence used for the apo-rA71 structure differs slightly from what is shown in (A) with a few stabilizing mutations in P1.
