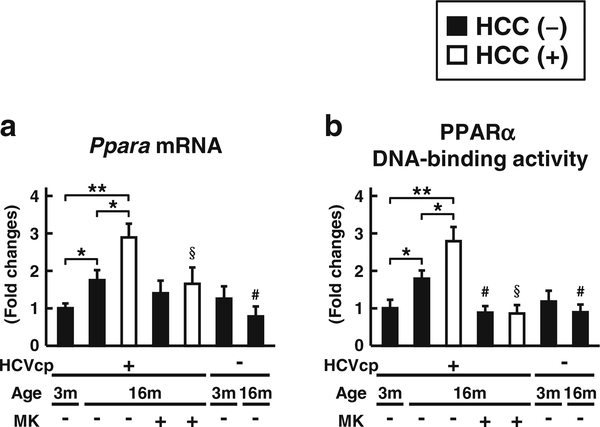
Fig. 4.
Changes in expression and DNA-binding ability of hepatic PPARα a The level of Ppara mRNA expression was measured in 3and 16-month-old HCVcpTg and non-Tg mice. Levels of mRNA expression were analyzed by qPCR and normalized to those of Gapdh mRNA. b The DNA-binding ability of PPARα was examined using 60 μg of nuclear liver protein. All data are shown as the fold changes to those of 3-month-old HCVcpTg mice and expressed as the mean ± SD (n = 6 for 3-month-old HCVcpTg mice; n = 6 for 16-month-old HCVcpTg mice without HCC; n = 5 for 16-month-old HCVcpTg mice with HCC; n = 6 for MK886-treated 16-month-old HCVcpTg mice without HCC; n = 4 for MK886-treated 16-month-old HCVcpTg mice with HCC; n = 4 for 3-month-old non-Tg mice; and n = 4 for 16-monthold non-Tg mice). Closed bars indicate non-tumor liver samples. Open bars indicate liver cancer samples. HCVcp, HCV core protein; HCC, hepatocellular carcinomas. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01; comparison among sample groups for the Tg or non-Tg mice. # p < 0.05; compared with non-treated age-matched Tg mice without HCC. §p < 0.05; compared with non-treated age-matched Tg mice with HCC