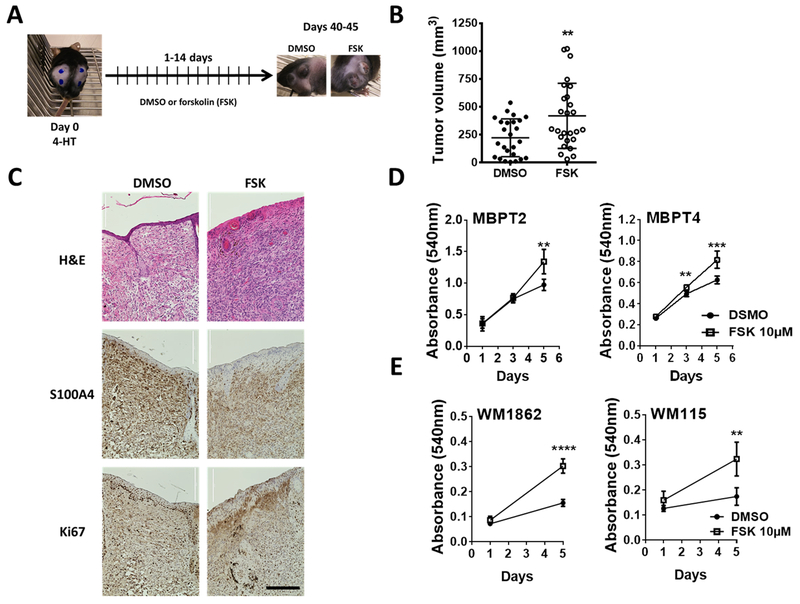
Fig. 1. cAMP signaling promotes melanoma tumor development and primary melanoma cell growth.
(A) Schematic of the experimental design for chemical activation of adenylate cyclases (ACs) in BrafCa/Pten−/− mouse melanoma model. 4-HT: 4-hydroxitamoxifen (5mM); forskolin 10mM (FSK): AC activator; DMSO: vehicle control. (B) Tumor volume 6 weeks (40 – 44 days) after the 4-HT application followed by 14 days of topical application of either AC activator FSK or DMSO. Data show volume calculated using the formula for a prolate ellipsoid, (length × width2)/2. DMSO: n = 7 (4 females, 3 males; 25 tumors); FSK: n = 7 (4 females, 3 males; 26 tumors). (C) Histology and immunohistochemical analysis of mouse melanoma tumors. S100A4 was used as a melanoma marker and Ki67 as a marker of proliferative cells. Scale bar: 400μm (D) MTT assay showing the growth of melanoma cells isolated from the vehicle-treated mouse tumor. FSK in the medium was replenished every 48 h throughout the experiment. Values (mean± SD) from 5-6 replicates are shown. (E) Effect of treatment with FSK on human primary melanoma cell lines was assessed by MTT assay as described for (D). DMSO: Control; FSK: AC activator forskolin. Data (mean ± SD) from 5-6 replicates analyzed by unpaired Student’s t test are shown. P values: * indicates P ≤0.05; ** ≤0.01; *** ≤0.001 and **** ≤0.0001.