Figure 2.
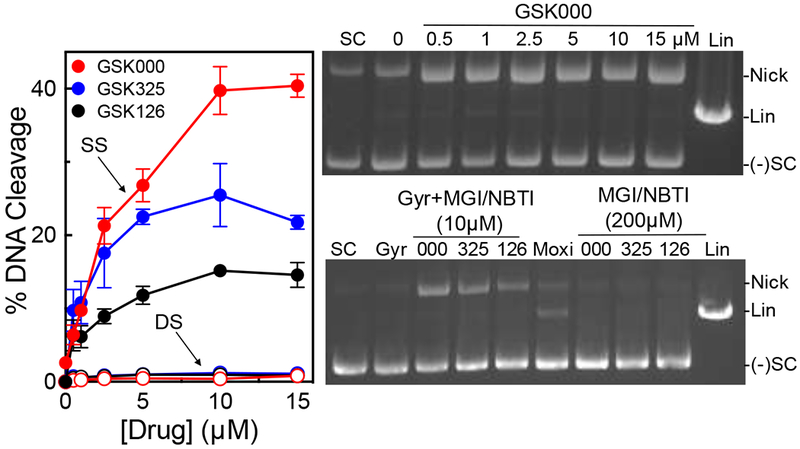
MGIs induce single-stranded DNA breaks mediated by M. tuberculosis gyrase. The left panel shows the quantification of single-stranded (SS, closed circles) and double-stranded (DS, open circles) DNA breaks induced by GSK000 (red), GSK325 (blue), or GSK126 (black) in the presence of M. tuberculosis gyrase. Error bars represent the standard deviation (SD) of four independent experiments. The top right gel shows DNA cleavage products produced by gyrase that was incubated with increasing concentrations of GSK000. The bottom right gel shows DNA products following cleavage reactions containing 10 μM GSK000 (000), GSK325 (325), or GSK126 (126), or 20 μM moxifloxacin (Moxi) in the presence of gyrase or 200 μM GSK000, GSK325, or GSK126 in the absence of enzyme. Negatively supercoiled (SC) and linear (Lin) DNA controls are shown along with a reaction that contained gyrase, but no drug (Gyr). The mobilities of negatively supercoiled DNA [(−)SC], nicked circular DNA (Nick), and linear DNA (Lin) are indicated. Gels are representative of at least four independent experiments.
