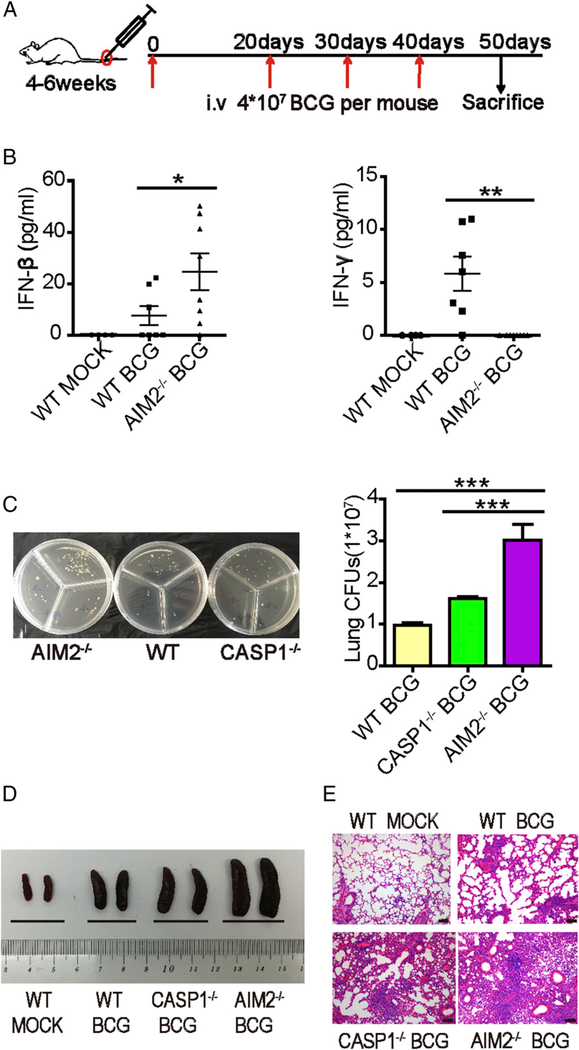
FIGURE 1.
AIM2-mediated inhibition of IFN-β production is necessary for controlling M. bovis (BCG) infection in vivo. WT, AIM2−/−, and Caspase-1−/− mice were infected with 4×107 CFU BCG four times. (A) Schematic diagram of the infection with BCG. (B) Levels of IFN-β and IFN-γ in the sera of WT and AIM2−/− mice, with or without BCG infection. (C) Bacterial CFU counts in the homogenates of lungs from BCG-infected WT, AIM2−/−, and Caspase-1−/− mice in a representative of two independent experiments. Five to six mice per group were used in the experiments, and two AIM2−/− mice died with extremely high CFU counts (outlier not included). Similar significance trends for comparisons between AIM2−/− and control groups were seen in the other experiment. (D) Gross pathology features of the spleens of two representative mice from each group infected with BCG. (E) Histopathology of the lungs from mice infected with BCG. Sections were stained with H&E and assessed. Scale bars, 100 μm. Data are representative of at least two independent experiments. The results are shown as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, Student t test.