Extended Data Figure 5. Comparison of interaction between FimD plug domain and NTD (a) and between FimD CTDs and FimCF (b) in Conformers 1 and 2 by superimposing the two conformations.
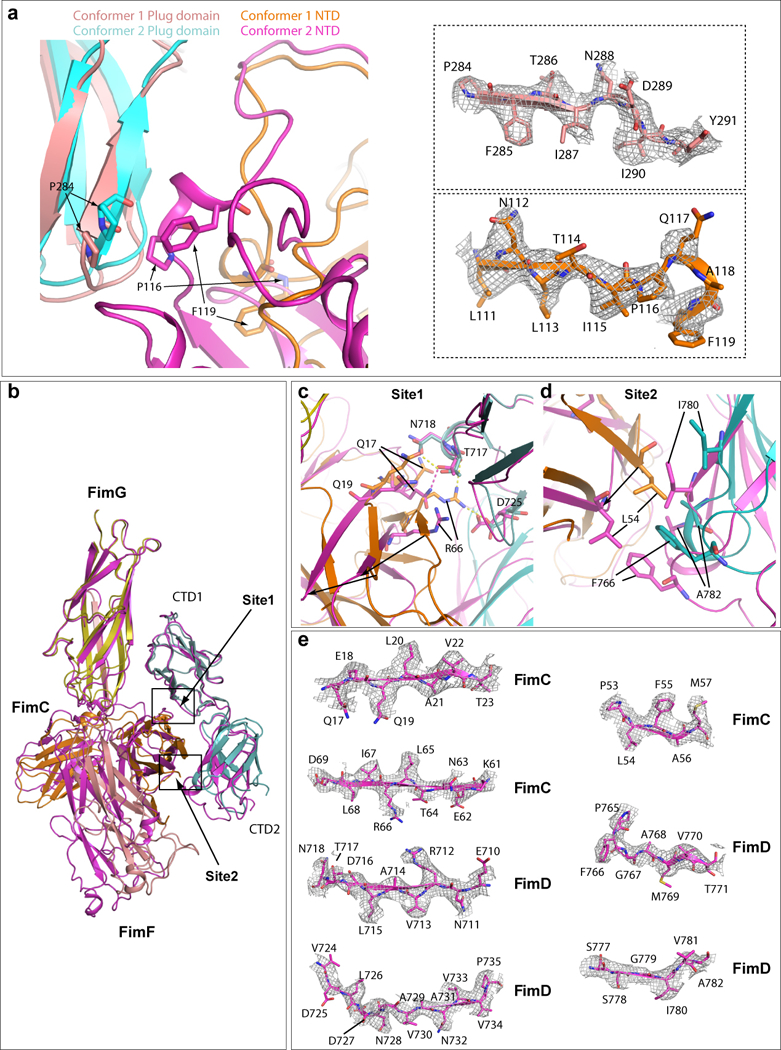
The Plug domain and NTD of Conformer 1 are colored in salmon and orange, respectively, and Plug domain and NTD of Conformer 2 in cyan and magenta, respectively. In the right side, electron densities of regions involved in the interaction in Conformer I are shown in the top panel (FimD plug) and bottom panel (FimD NTD). Some amino acids have clear side-chain densities. (b) Superimposition of FimD_CTDs-FimCF in Conformers 1 (magenta). and 2 (colored as in Fig. 3). (c) Detailed interactions in Site 1. Extensive interactions are present in Conformer 2. Much weaker interactions are present in conformer 1 (between Q17 and T717). (d) Detailed interactions in Site 2 (marked in panel a). In Conformer 2, hydrophobic interactions exist between FimC L54 and FimD F766, and between I780 and A782. Much weaker interactions are present in Conformer 1. (e) The electron densities in regions involved in Sites 1 and 2 interactions between FimC and FimD in Conformer 1. Some amino acids have side-chain densities.
