Figure 3.
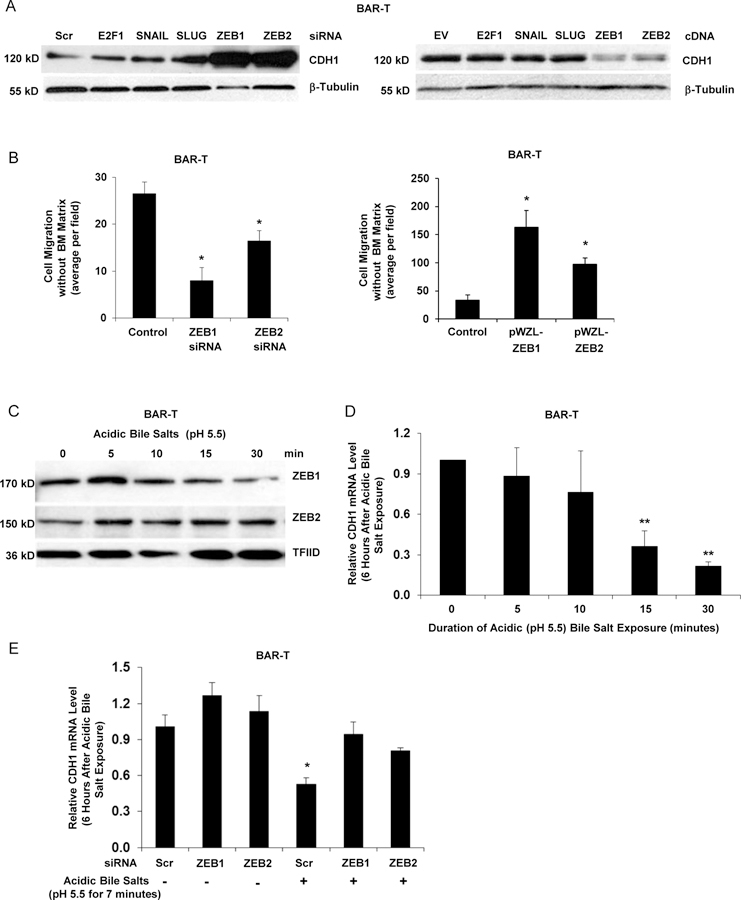
ZEB1 and ZEB2 regulate features of EMT in response to acidic bile salt exposure in non-neoplastic Barrett’s cells. (A) Western blot for CDH1 at 72 hours following siRNA knockdown or cDNA expression of SNAIL, SLUG, ZEB1 or ZEB2; β-tubulin served as a loading control. Scrambled (Scr) siRNA, empty vector (EV) and non-related E2F1 served as controls. (B) Cell migration with knockdown (left panel) or stable overexpression (right panel) of ZEB1 or ZEB2. (C) Western blot for nuclear levels of ZEB1 and ZEB2 immediately following exposure to acidic bile salts for times ranging from 5–30 minutes; TFIID served as a loading control. Representative qPCR for CDH1 mRNA level 6 hours after exposure to acidic bile salts for times ranging from 5–30 minutes relative to untreated (0 minutes) cells without (D) and with (E) knockdown of ZEB1 or ZEB2; qPCR assays were performed in triplicate in at least two independent experiments. Bar graphs depict the mean ± SEM. *p<0.05 and **p<0.01 compared with control, 0 minutes, or non-acidic bile salt treated Scr siRNA. In B &E, cells were transfected with siRNAs for 72 hours. For cell migration assays in B, bar graphs depict the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments.
