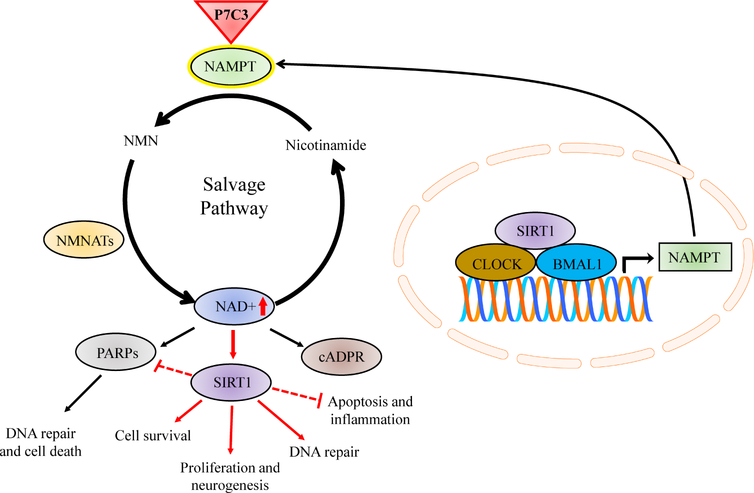
Figure 3.
NAD+ biosynthesis via the salvage pathway, circadian regulation, and P7C3-mediated NAMPT enhancement. NAMPT (green) catalyzes the conversion of nicotinamide to NMN, which is then converted to NAD+ (dark blue) through the activity of NMNATs (yellow). NAD+ is a critical cosubstrate for the downstream enzymatic activity of PARPs, SIRTs, and cADPR synthases, which have extensive influence on cellular function, viability, and organism homeostasis. The circadian clock and NAD+-dependent SIRT1 (purple) regulate the transcription of NAMPT (right inset). Oscillations in NAMPT levels rely on SIRT1 transcription, maintaining a positive feedback cycle between NAMPT, NAD+, and SIRT1. P7C3 compounds (red triangle) bind to and enhance the activity of neuronal NAMPT thereby increasing cellular NAD+ levels. NAD+-mediated neuroprotection implicates SIRT1 signaling cascades, critical prosurvival pathways governing a multitude of cellular processes associated with viability, repair, inflammation, and neurogenesis. BMAL1, brain muscle ARNT-like protein 1; cADPR, cyclic ADP (adenosine diphosphate) ribose; CLOCK, circadian locomotor output cycles kaput; NAD, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; NAMPT, nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase; NMN, nicotinamide mononucleotide; NMNAT, nicotinamide mononucleotide adenylyltransferease; PARP, poly ADP ribose polymerase; SIRT1, sirtuin-1.