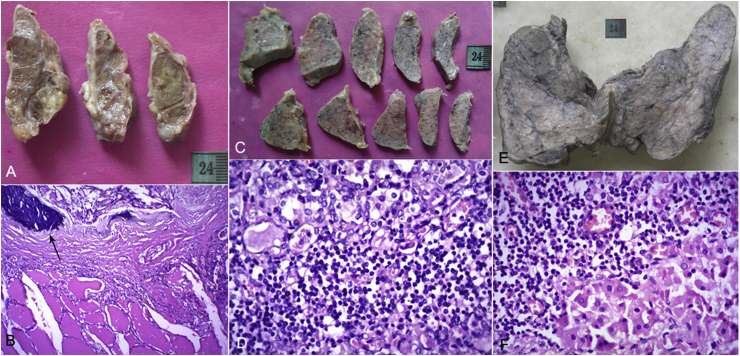
Fig. 1.
Multinodular goiter: (A) the right lobe of the thyroid has been serially sectioned to show multinodularity. Note the absence of enlargement; (B) one of the nodules is well delineated and shows the presence of calcification (arrow, H&E 400×); lymphocytic thyroiditis: (C) Both the lobes of the thyroid have lost their normal pale brown honey-combed appearance and are fleshy and whitish; (D) the whitish appearance was because of the presence of aggregates and infiltrates of lymphocytes (H&E 400×); Hashimoto's thyroiditis: (E) the thyroid is uniformly enlarged and shows a fleshy, lobulated, gray-white cut surface; (F) apart from lymphocytic aggregates, the follicles show oncocytic metaplasia (Hurthle cell change, H&E 400×). H&E, hemotoxylin and eosin.