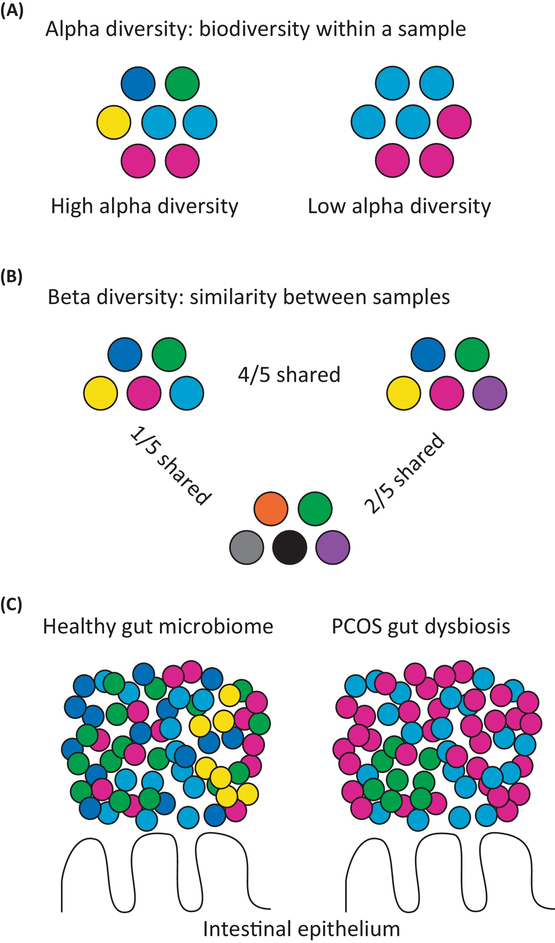
Figure 1.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) Is Associated with Changes in the Gut Microbiome. Comparisons of alpha and beta diversity between hypothetical, gut microbial communities. Different bacterial taxa are represented by circles with different colors. (A) Alpha diversity represents the biodiversity (species richness) within a specific community or individual sample. The sample on the left has high alpha diversity (five bacterial taxa), while the sample on the right has low alpha diversity (two bacterial taxa). (B) Beta diversity represents how similar one community or individual sample is to another. The samples on the left and right are similar to each other (4/5 shared bacterial taxa), while the sample on the left is not very similar to the sample in the middle (1/5 shared bacterial taxa). (C) PCOS is associated with a microbial imbalance or dysbiosis compared with the healthy state including lower alpha diversity and changes in the relative abundance of bacteria from the Bacteroidaceae, Clostridiaceae, Erysipelotrichidae, Lachnospiraceae, Lactobacillaceae, Porphyromonadaceae, Prevotellaceae, Ruminococcaceae, and S24–7 families.