Figure 3:
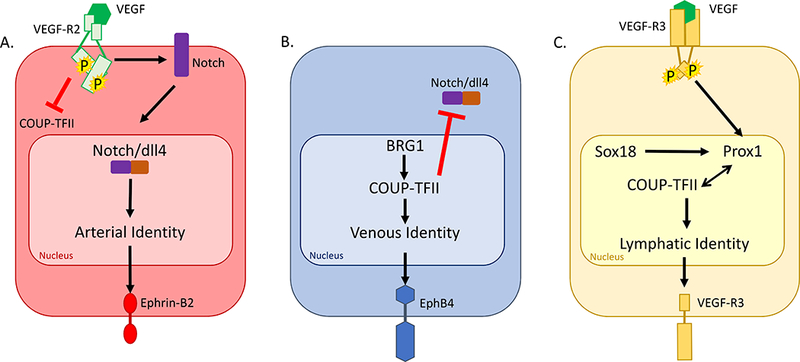
Cell signaling determines the molecular determinants of endothelial cell identity. A. Binding of VEGF to the VEGFR-2 receptor induces Notch activation; the cytoplasmic domain of Notch is cleaved and interacts with dll4, and together they translocate to the nucleus. Activation of arterial gene expression results in Ephrin-B2 expression on the endothelial cell surface. B. Transcription of COUP-TFII is induced in part by BRG1. COUP-TFII is a transcription factor that results in Eph-B4 expression on the endothelial cell surface. C. Binding of VEGF to the VEGFR-3 receptor results in upregulation of Prox1. Prox1 forms a heterodimer with COUP-TFII to induce lymphatic identity with VEGFR-3 expression on the endothelial cell surface.
