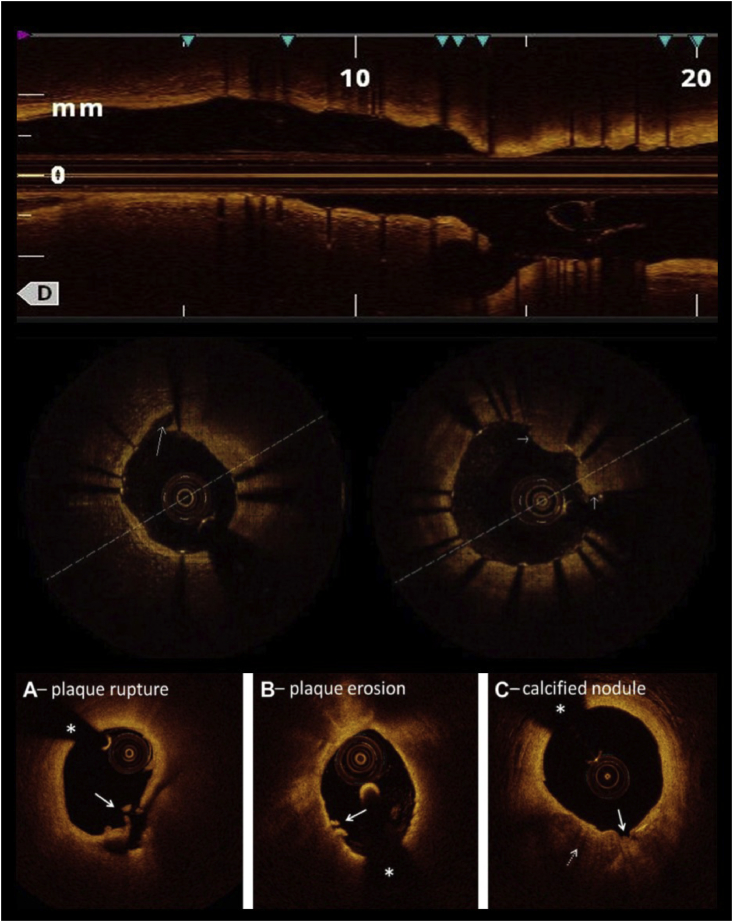
Fig. 4.
Top, OCT pullback after stenting showing longitudinal view of the vessel. Stent length can be measured and side-branch ostium visualized. The same view can be used pre-PCI to decide stent length and landing zones. Middle left, stent edge dissection as seen on OCT (long arrow). Middle right, tissue prolapse through stent struts (short arrows). Bottom, OCT findings in acute coronary syndrome. (A) Plaque rupture is defined as a lipid plaque with fibrous cap discontinuity (arrow) and cavity formation inside the plaque. (B) Definite plaque erosion is defined by the presence of attached thrombus (arrow) overlying an intact and visualized plaque. (C) Calcified nodules are defined by fibrous cap disruption (solid arrow) with underlying calcified plaque (dotted arrow) characterized by protruding calcification, superficial calcium, or the presence of significant calcium adjacent to the lesion. The asterisks denote guidewire shadow artifact. OCT, optical coherence tomography.