Figure 2.
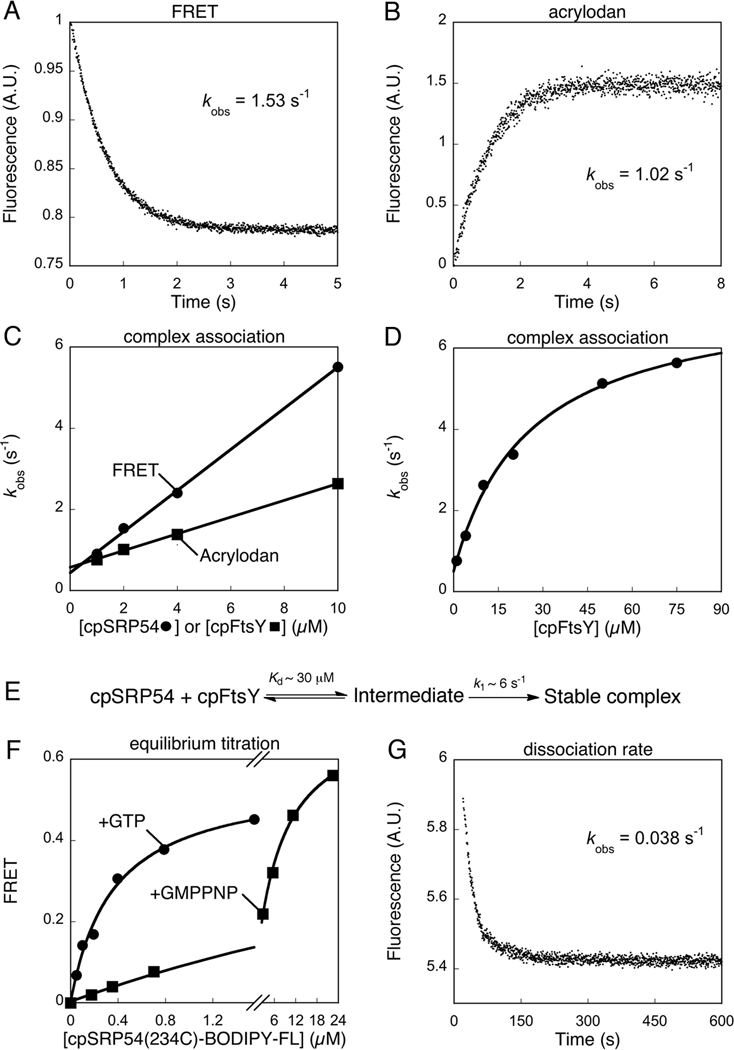
Thermodynamic and kinetics for formation of the cpSRP54•cpFtsY complex. (A) Complex assembly between 0.5 μM cpFtsY(321C)-DACM and 2 μM cpSRP54(234C)-BODIPY-FL, measured in a stopped-flow apparatus as described in Methods. Single exponential fit of the data gave a kobs value of 1.53 s-1. (B) Complex assembly between 0.5 μM cpSRP54(234C)-acrylodan and 2 μM cpFtsY, measured in a stopped-flow apparatus as described in Methods. Single exponential fit of the data gave a kobs value of 1.02 s-1. (C) Association rate constants for cpSRP54-cpFtsY complex formation with GTP measured by FRET (●) and acrylodan fluorescence (■). Linear fits of the data gave complex assembly rate constants (kon) of 5 × 105 and 1.57 × 105 M−1 s−1 with FRET and acrylodan fluorescence, respectively. (D) A hyperbolic dependence of complex assembly rate constants on cpFtsY concentration. The data were fit to Eq. 4 in the Methods, which gave a Kd value of 30 μM and a rate constant of 6 s−1 at saturating cpFtsY. (E) A two-step schematic of cpSRP54-cpFtsY complex assembly. (F) Equilibrium titration of the cpSRP54•cpFtsY complex formed with GTP (●) or GMPPNP (■) measured by FRET. Complex formation with GTP was carried out using mutant cpFtsY(A168W) to minimize GTP hydrolysis. The data were fit to Eq. 2, which gave Kd values of 0.35 μM with GTP and 7 μM with GMPPNP. (G) Dissociation kinetics of the cpSRP54(234C, A142W)•cpFtsY complex, measured as described in the Methods. Single exponential fit of the data gave an apparent dissociation rate constant of 0.038 s-1. After subtracting the GTP hydrolysis rate from this complex (0.008 s−1), the corrected dissociation rate constant was 0.030 s-1.
