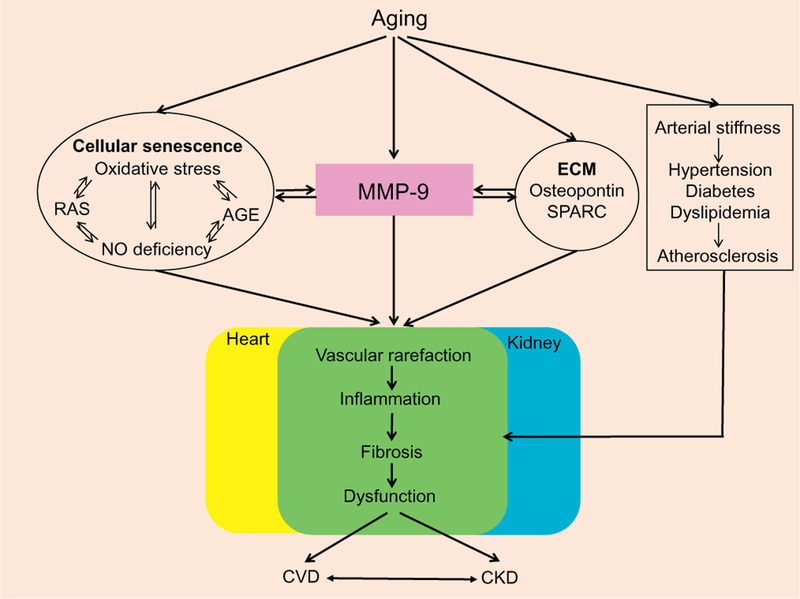
Fig. 3.
Mechanistic diagram showing effects of macrophage-derived matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-9 in cardiorenal aging. In addition to reported common aging mechanisms such as oxidative stress, renin-angiotensin system (RAS), nitric oxide (NO) deficiency, and advanced glycation end product (AGE), all of which cause cellular senescence, and extracellular matrix (ECM) components including osteopontin and secreted protein acidic and rich in cysteine (SPARC), macrophage-derived MMP-9 causes inflammation and fibrosis dependent and independent vascular rarefaction in the heart and kidney. Age-related systemic changes and comorbidities of risk factors (hypertension, diabetes, dyslipidemia) facilitates cardiorenal aging. Cardiovascular disease (CVD) and chronic kidney disease (CKD) interact each other, exacerbating their dysfunctional changes.