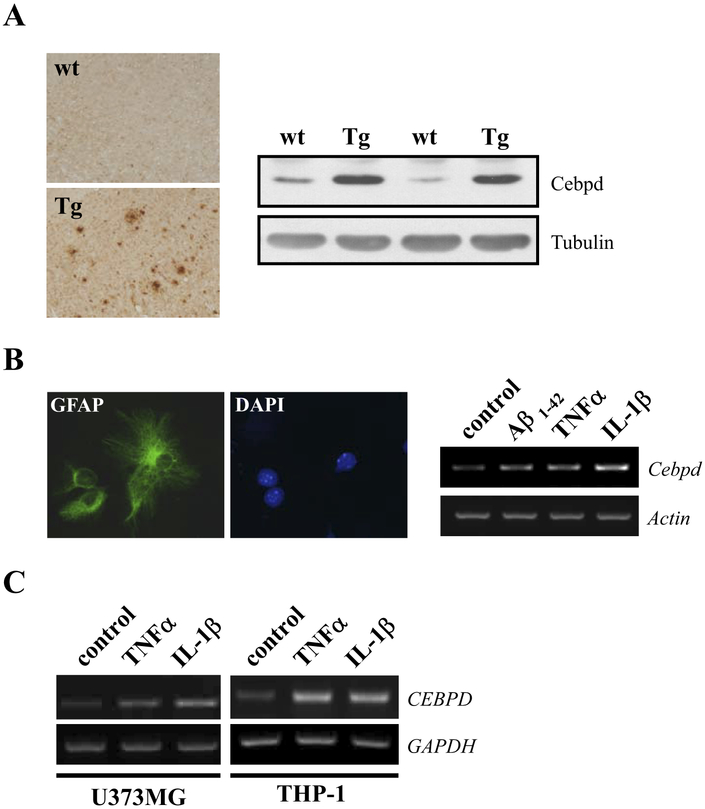
Fig. 1.
CCAAT/enhancer binding protein delta (CEBPD) expression is induced in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) models and by proinflammatory cytokines. (A) Sagittal sections and protein lysates of brain cortex were prepared from wild type (wt) and APP transgenic (Tg) mice, and subjected to immunohistochemistry with β-amyloid (Aβ) antibody (left panel) or Western blot analysis with Cebpd antibody (right panel), respectively. (B) Enriched mouse primary glial cultures were derived from mice cerebral cortex and the glial cells were identified by immunofluorescence staining with GFAP antibody (left panel). Glial cells were then treated with 5 μM Aβ1–42, 20 ng/mL tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), or 5 ng/mL interleukin (IL)-1β for 3 hours, and reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) assay was performed to examine the expression of Cebpd mRNA (right panel). (C) U373MG and THP-1 cells were treated with 20 ng/mL TNF-α or 5 ng/ml IL-1β for 3 hours and Cebpd mRNA expression was examined by RT-PCR.