Figure 2:
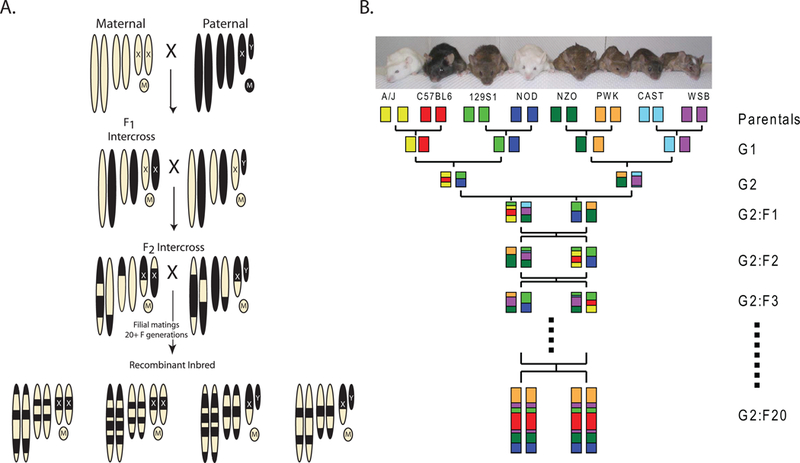
Strategies to generate Recombinant Inbred (RI) panels and the Collaborative Cross. A) Mating strategy to generate a standard RI panel. The chromosomes of the maternal strain are depicted by the tan ovals. The paternal strain chromosomes are black. Mitrochondrial genomes are depicted by circles with M’s. The resulting RI panel substrains are inbred chimeras of the original two parental strains, as indicated at the bottom of the figure. RI panels usually consist of 13–75 substrains (RI strains – The Jackson Laboratory, http://www.jax.org/smsr/ristrain.html) (Box 1). B) The eight-way funnel breeding design of the Collaborative Cross. One example of the funnel design is shown here. Additional funnels are generated by changing the position of the parental strains at the top of the funnel. The genomes of each of the eight progenitor strains are indicated by colored boxes. The funnel design incorporates all eight genomes randomly until inbreeding begins after the G2:F1 generation. The ultimate goal of the CC is to generate more than a hundred sublines. Current status of the CC can be found at the Collaborative Cross Status website (http://csbio.unc.edu/CCstatus/index.py).
