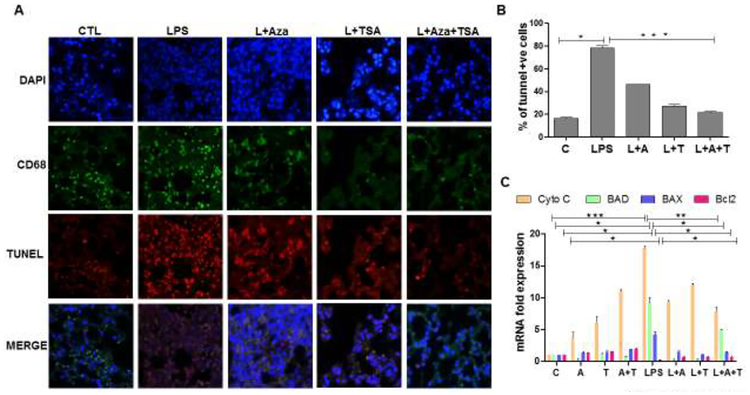
Figure 6. The effect of Aza and TSA treatment decreases the number of TUNEL positive cells in lung tissues from LPS challenged mice.
(A) Cell death was measured by TUNEL staining, and macrophages were identified by the macrophage surface marker, CD68. The TUNEL positive BMDMs were assessed by counting the number of triple-positive cells as a result of co-localization of TUNEL (red), CD68 (green) and DAPI (blue). (B) Quantification of triple-positive apoptotic cells. LPS group shows an increased number of TUNEL positive BMDMs. These numbers are significantly reduced in the control group, and treatment with Aza and TSA groups. (C) qRT-PCR data show that Aza and TSA treatment significantly reduced LPS-induced apoptotic gene expression (cytochrome C, BAD and BAX) when compared with no treatment or treatment with Aza alone or TSA alone in BMDMs challenged with LPS after 24 hours. There is an increased expression of anti-apoptotic genes (Bcl2) in BMDMs treated with Aza and TSA after LPS challenges. Data are expressed as means ± SEM, n =3 (C). *P<0.05, **P< 0.01, ***P < 0.001. A, Aza; T, TSA; L, LPS.