Figure 2. Developmental Defect of Embryos.
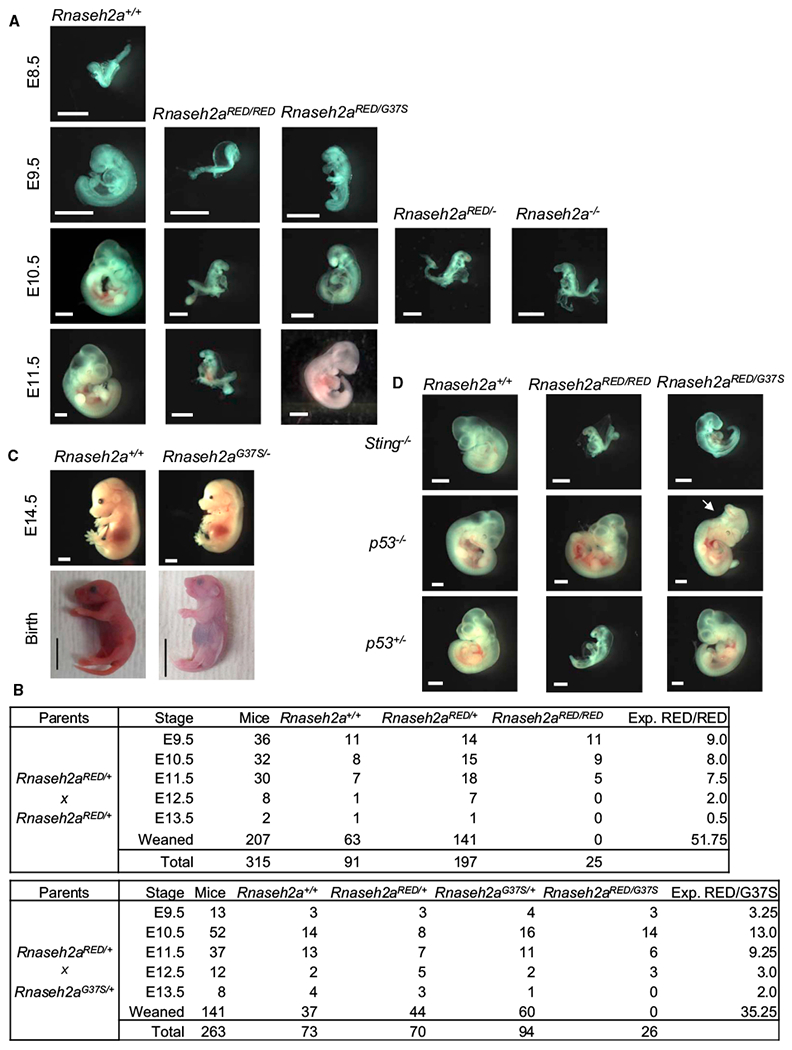
(A) Rnaseh2a+/+, Rnaseh2aRED/RED, Rnaseh2aRED/G37S, Rnaseh2aRED/−, and Rnaseh2a−/− embryos at embryonic days 8.5–11.5. Scale bar, 1 mm.
(B) Survival of mouse embryos from crosses of Rnaseh2aRED/+ × Rnaseh2aRED/+ (top) and Rnaseh2aRED/+ × Rnaseh2aG37S/+ (bottom). Expected number of Rnaseh2aRED/RED and Rnaseh2aRED/G37S at Mendelian ratio is shown in right column.
(C) Rnaseh2a+/+ and Rnaseh2aG37S/− embryos and neonates. Scale bars, 2 mm (E14.5) and 1 cm (birth).
(D) Partial rescue of embryonic lethality by ablation of p53 gene. Images of E10.5 embryos are shown. A morphological rescue of Rnaseh2aRED/RED and Rnaseh2aRED/G37S was observed on p53 background. Rnaseh2aRED/G37S was also rescued on p53+/− background (n = 5), whereas Rnaseh2aRED/RED was not (n = 3). No rescue of Rnaseh2aRED/RED (n = 8) and Rnaseh2aRED/G37S (n = 5) phenotypes was observed on Sting−/− background.
