Fig. 3. CRAC current (ICRAC) in ICC.
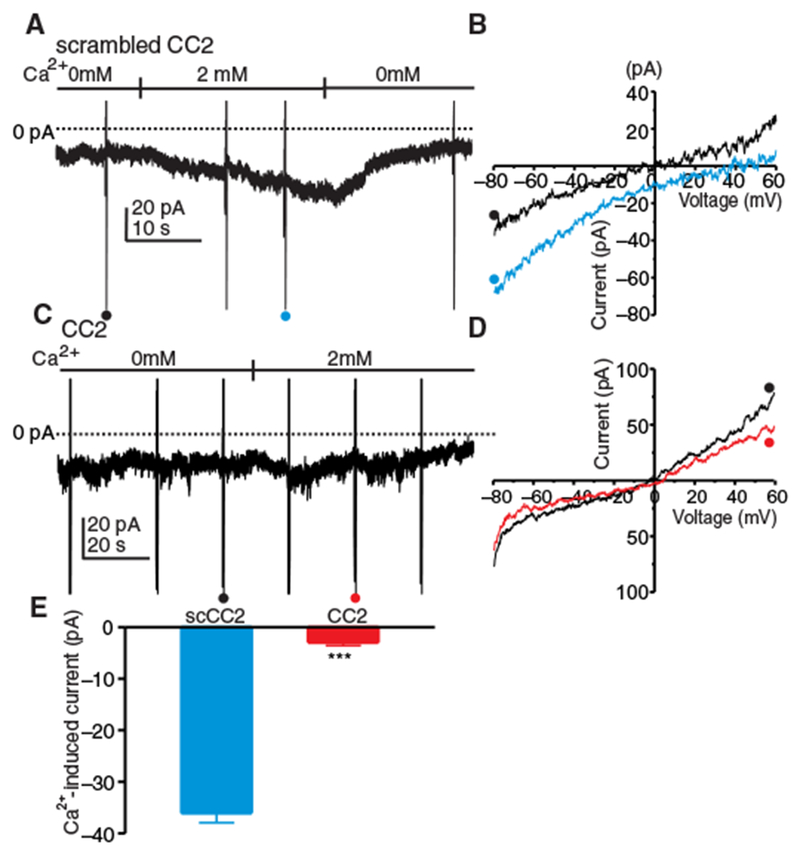
(A) ICC were held at −50 mV in whole-cell voltage-clamp and exposed to Ca2+-free external solution (solution II) with NPPB (30 μM) and thapsigargin (1 μM) for 10 min to deplete ER Ca2+ and block CaCC and dialyzed with Cs+-rich solution containing BAPTA (solution VI). Inward current developed in cells dialyzed with scrambled CC2 peptide (10 μM) upon reintroduction of 2 μM [Ca2+]o. Ramp potentials from −80 to +60 mV were run before and after addition of 2 mM [Ca2+]o (examples noted by • and •). (B) Current responses to ramp potentials in (A) [• (black trace) is control, and • (blue trace) is after addition of 2 mM [Ca2+]o]. (C) ICC were held at −50 mV in whole-cell voltage-clamp, treated with Ca2+-free external solution (solution II) with NPPB (30 μM) and thapsigargin (1 μM) for 10 min to deplete ER Ca2+ and block CaCC, and dialyzed with Cs+-rich solution containing BAPTA (solution VI). (D) Responses to ramp potentials in (C) [• (black trace) is control, and • (red trace) is after addition of 2 mM [Ca2+]o]. (E) Summary data showing the effects of scrambled CC2 peptide and CC2 peptide on current induced at −80 mV by reintroducing 2 mM [Ca2+]o. Data are means ± SEM (n = 5 cells for each group; ***P < 0.001, Student’s two-tailed t test).
