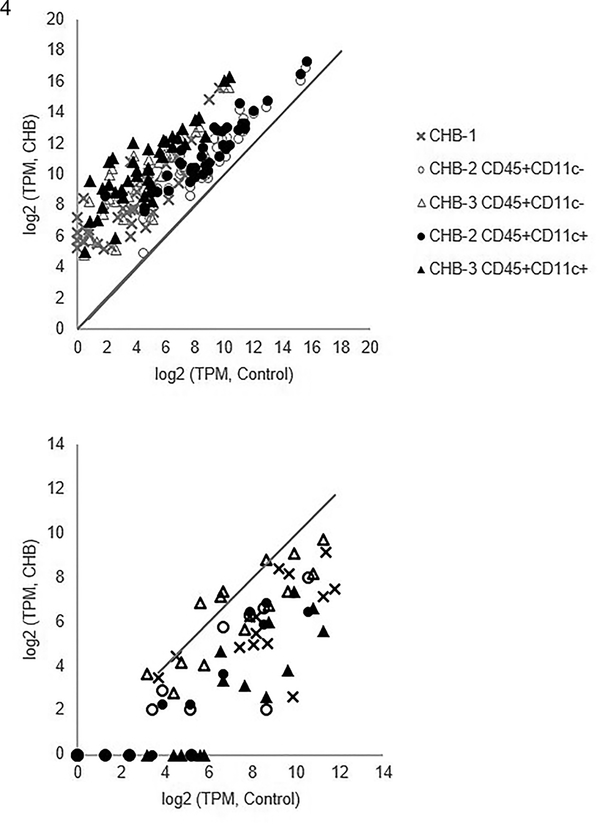
Figure 4. Agnostic survey of genes of flow-sorted human leukocytes derived from CHB and healthy fetal hearts.
Shown are log2 transformed transcripts per million (TPM) of CHB leukocyte populations (y-axis) and log2 transformed TPM of the same genes within control leukocyte populations (x-axis) using values of CHB-1, CHB-2, and CHB-3 with corresponding control values (Control-1, Control-2, and Control-3, respectively). The upper and lower panels correspond to genes within the GO categories Extracellular region and Integral component of plasma membrane, respectively. The solid line in both panels represents equivalent expression between CHB and control leukocytes. In the upper panel, the transcripts within the Extracellular region GO module are significantly elevated in CHB leukocytes compared to control. Among the 39 upregulated genes within this category (ELN, EDN1, CX3CL1, MMP2, EPHB2, NOV, OLFML1, ACE, BCHE, PAPPA, FNDC1, GDF6, COL27A1, SERPINE1, COL6A3, CFH, COL6A1, AGRN, IGFBP5, BMP6, COL8A1, NRG1, THBS2, BMP4, SVEP1, STC2, EFEMP1, HSPG2, COL5A3, SLIT3, PRELP, SIGLEC1, VEGFC, BGN, COL1A2, COL1A1, ADAMTS2, MFAP5, and PLA2G), note that EDN1, MMP2, and SERPINE1 have been associated with CHB in prior studies (6, 24). Of the top ten upregulated genes in the CHB leukocytes as ranked by fold increase of expression (Table 4), half were reported within this GO category (MMP2, EPHB2, MFAP5, NOV, and SIGLEC1). For the lower panel, the genes within the Integral component of plasma membrane GO module are significantly lowered in CHB leukocytes compared to control. Three of the ten most steeply down-regulated genes in the CHB leukocytes as ranked by fold decrease in expression (Table 5, PTGDR2, CD1C and CD1E) are among the 14 underexpressed genes within this category (FCER1A, LTK, CXCR5, CD40LG, CD8B, ST14, CD1C, MS4A2, MAL, CD1A, PTGDR2, CD1E, CD1D, and SLC14A2).