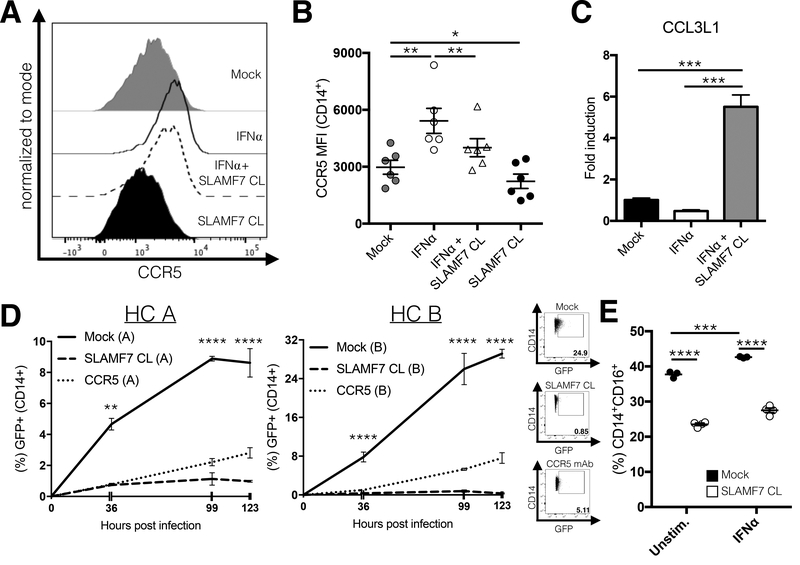
Figure 6.
SLAMF7 activation inhibits monocyte infection with HIV-1 in vitro and down-regulates CD16. (A and B) PBMCs from HIV+ individuals (n=6) were stimulated in vitro with IFN⍺ and the SLAMF7 receptor was activated by cross-linking where indicated. Surface expression of CCR5 was measured by flow cytometry. (C) mRNA expression of CCL3L1 was assessed by qRT-PCR from the same samples in (Fig. 5A and B). (D) Isolated monocytes from 2 HCs (labeled “A” and “B”) were infected with HIV-1-Ba-L-GFP and infectivity was assessed at the indicated time points by FACS. Two technical replicates for each HC were analyzed. A CCR5 blocking mAb (10 μg/mL) was included as a positive control. (E) PBMCs from a single HC were stimulated in vitro as indicated for 24 hours before analysis by flow cytometry. This experiment used 25 IU/mL IFN⍺. Percent indicated on y-axis is from all cells in FSC-A/SSC-A “monocyte” gate. (B and C) Groups compared using a 1-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test. (D and E) Groups compared using a 2-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test. Data presented as mean ± SEM and are representative of 1 experiment (B and C) or 2 independent experiments showing similar results (D and E). *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001.