Fig. 1. RIPK3+/D161N fetuses on a RIPK1-deficient background exhibit MLKL-dependent lethality.
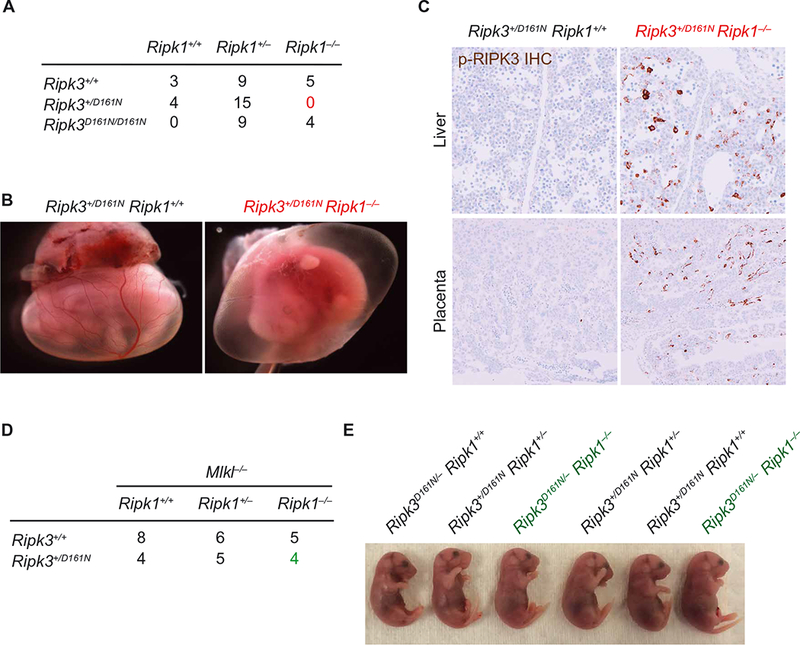
(A) Number of embryonic day 18.5 (E18.5) embryos recovered from intercrossing Ripk1+/− Ripk3+/D161N mice. Data are pooled from the analysis of 10 independent litters. (B) Whole-mount embryo imaging of E12.5 littermates. Images are representative of at least four embryos analyzed of each genotype analyzed between E12.5 and E13.5. (C) Immunohistochemical (IHC) analysis of phosphorylated RIPK3 in tissue sections from E11.5 placenta and liver. Images are representative of greater than three independent controls and three Ripk1−/−Ripk3+/D161N embryos. (D) Number of E18.5 embryos from crossing of Ripk1+/− Ripk3+/D161N Mlkl−/− and Ripk1+/− Ripk3+/+ Mlkl−/− mice. Data are pooled from the analysis of six independent litters. (E) Images of E18.5 littermates recovered from intercrossing Ripk1+/− Ripk3+/D161N and Ripk1+/− Ripk3+/− mice. Images are representative of the analysis of at least two independent litters.
