Fig. 3. Necroptosis is impaired by kinase domain dimerization–defective RIPK3.
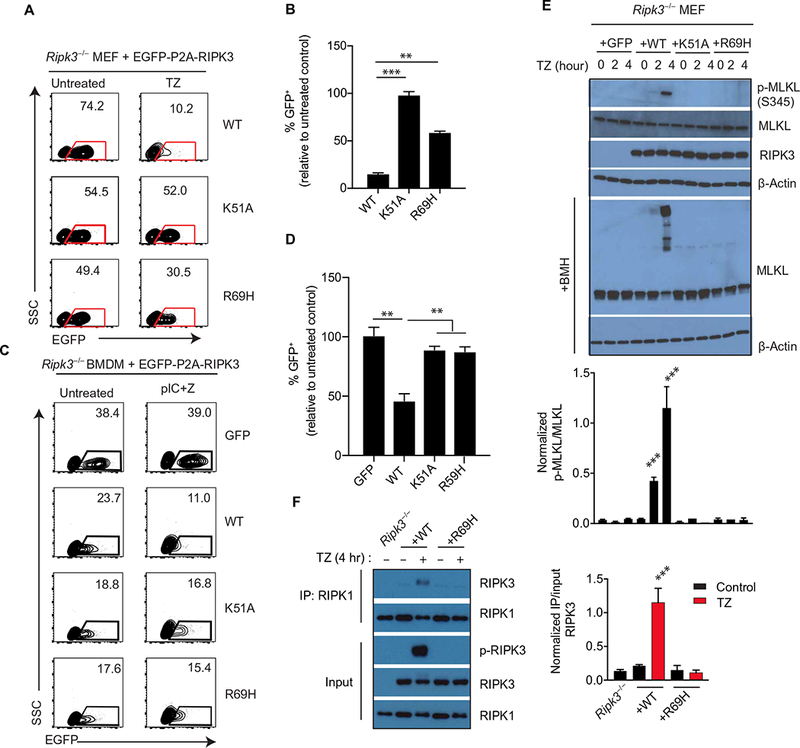
(A and B) Flow cytometry analysis of enhanced GFP (EGFP) abundance in Ripk3−/− MEFs infected with lentiviruses encoding EGFP-P2A-WT RIPK3 or the indicated mutants and treated with TNF-α + z-VAD-fmk for 24 hours. Dot plots (A) are representative of at least three independent experiments. The relative frequencies of GFP+ cells (B) are means ± SD from all experiments. SSC, side scatter. (C and D) Flow cytometry analysis of EGFP abundance in Ripk3−/− bone marrow cells transduced with lentiviral constructs encoding EGFP-P2A-WT RIPK3 or mutants and cultured for 6 days in macrophage colony- stimulating factor (M-CSF) to generate macrophages before treatment with poly(I:C)/z-VAD-fmk for 24 hours. (C) Dot plots (left) are representative of at least three independent experiments. The relative frequencies of GFP+ cells (D) are means ± SD from all experiments. (E) Western blot analysis for p-MLKL, MLKL, RIPK3, and β-actin from lysates of Ripk3−/− MEFs transduced with the indicated RIPK3 mutant construct and treated with TZ for the indicated times. Cell lysates were cross-linked with bismaleimidohexane (BMH) or directly used for immunoblotting. Blots are representative of at least three independent experiments. Normalized band intensities are means ± SD from all experiments. (F) Co-immunoprecipitation analysis of RIPK1 interactions in lysates of Ripk3−/− MEFs reconstituted with WT RIPK3 or RIPK3 R69H and treated with TZ for 4 hours that were immunoprecipitated for RIPK1. Blots are representative of at least three independent experiments. Normalized band intensities are means ± SD from all experiments. **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.005 by Student’s t test.
