Fig. 4. RIPK3 functions as an allosteric activator dependent on kinase domain homodimerization.
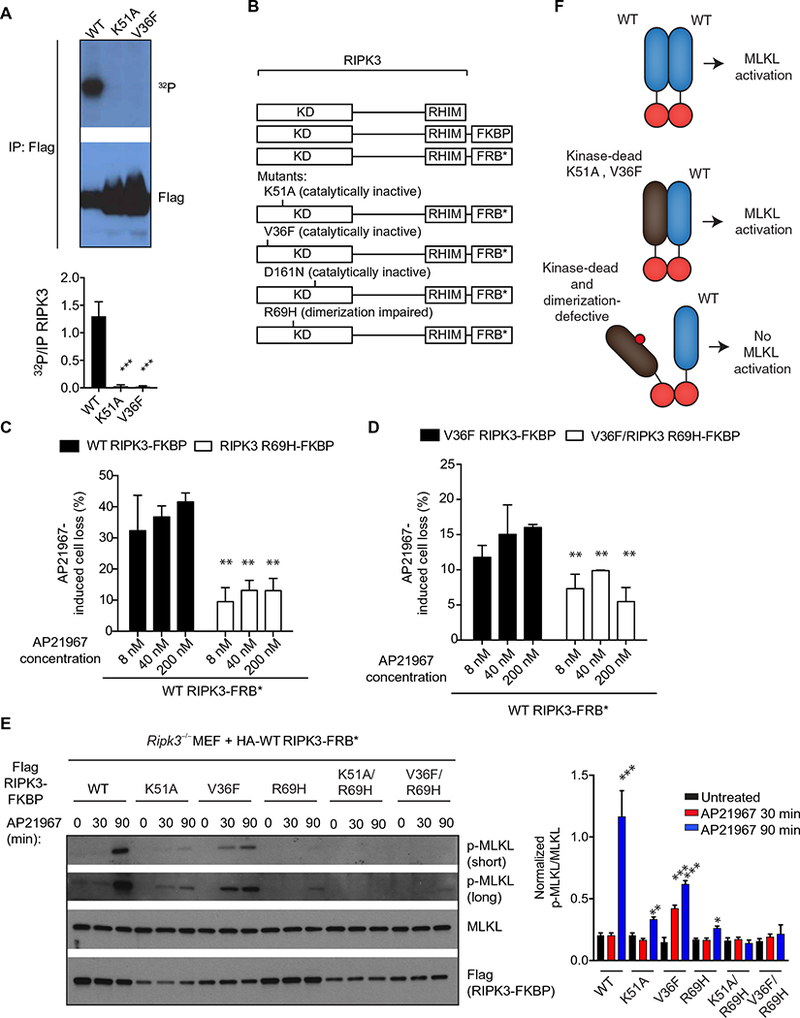
(A) Autoradiography and Western blot analysis of the in vitro kinase activity from lysates of HEK293T cells transfected with pcDNA3-Flag WT, pcDNA3-Flag K51A, or pcDNA3-Flag V36F RIPK3 constructs and immunoprecipitated for Flag 48 hours later. Blots are representative of at least three independent experiments. Normalized band intensities are means ± SD from all experiments. (B) Ripk3−/− MEFs were cotransduced with the indicated lentiviral constructs of RIPK3 fused to FRBP and FRB (B), which heterodimerize in the presence of AP21967. (C and D) CellTiter-Glo analysis of cellular viability in cells that received the indicated constructs and were pretreated with z-VAD-fmk for 1 hour before treatment with AP21967 for 6 hours. Data are means ± SD from three independent experiments. (E) Western blot analysis for p-MLKL, MLKL, and Flag in lysates from cells that received the indicated constructs and were pretreated with z-VAD-fmk before the addition of 250 nM AP21967 for the indicated time periods. Blots are representative of at least three independent experiments. Normalized band intensities are means ± SD from all experiments. (F) Model for allosteric activation of RIPK3 through kinase domain dimerization. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.005 by Student’s t test.
