Figure 4.
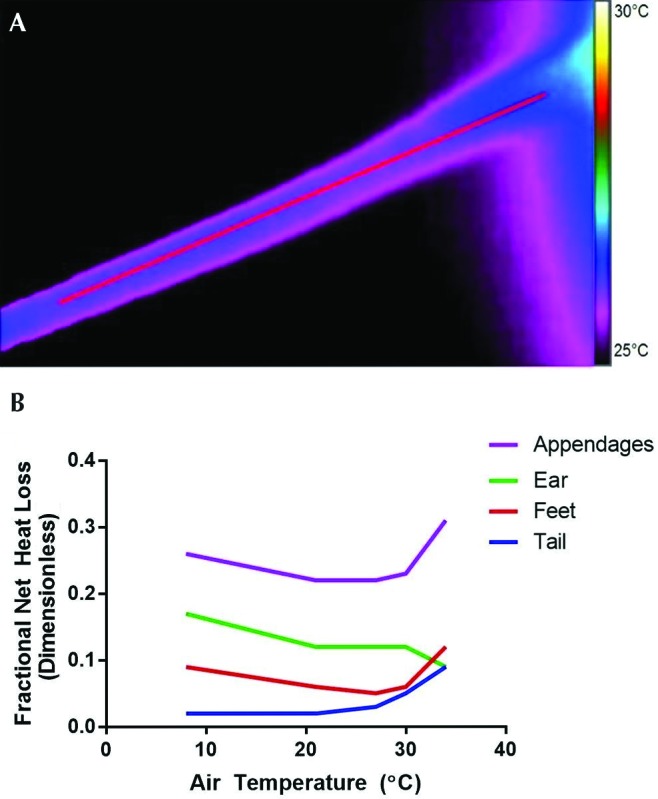
(A) Thermal image of a mouse tail at an ambient temperature of 21 °C, with a colored scale of temperature. The tail base is to the right of the image. (B) Fractional net heat loss as a function of air temperature; this illustration demonstrates the central role of temperature-dependent vasoconstriction and dilation in the tail and paws—but not ears—in thermal conservation by a similarly sized mouse species (Peromyscus maniculatus). Modified with permission from reference 24.
