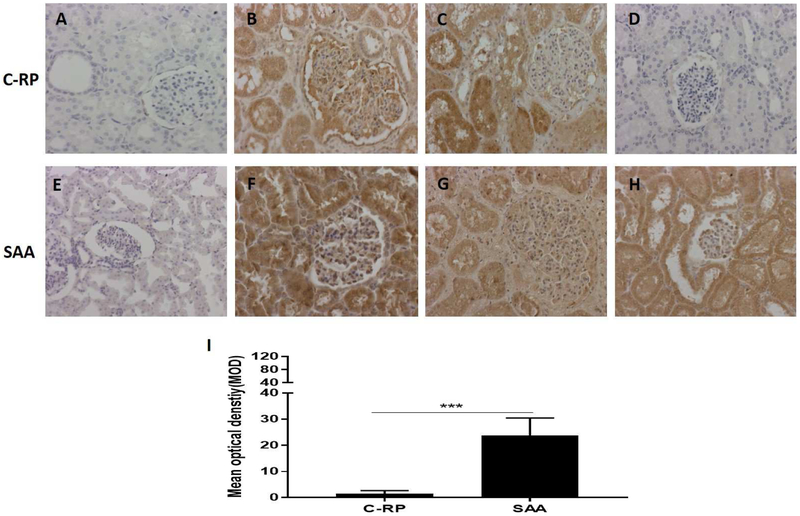
Figure 4: Deposition of C-RP (above) and amyloid A (below) in kidney tissue detected by IHC (magnification x200).
(A, E) Expression of C-RP and amyloid A in a naive pig kidney (negative control); (B, F) Deposition of C-RP and amyloid A in the pig kidney in a baboon that experienced anaphylactic shock (without transplantation) (positive control). (C, G) Deposition of C-RP and amyloid A in a pig kidney xenograft that underwent hyperacute rejection after transplantation into a baboon (while receiving the IL-6R inhibitor, tocilizumab, and the TNF-α antagonist, etanercept) (positive control). (D, H) Deposition of C-RP and amyloid A in a representative pig kidney xenograft (in a baboon with rejection, while receiving tocilizumab). There is considerable deposition of amyloid A, but not C-RP, in the kidney. (I) Comparison of C-RP and amyloid A deposition in pig kidney xenografts in baboons (that were receiving tocilizumab). The difference in deposition is significant (***p<0.001).