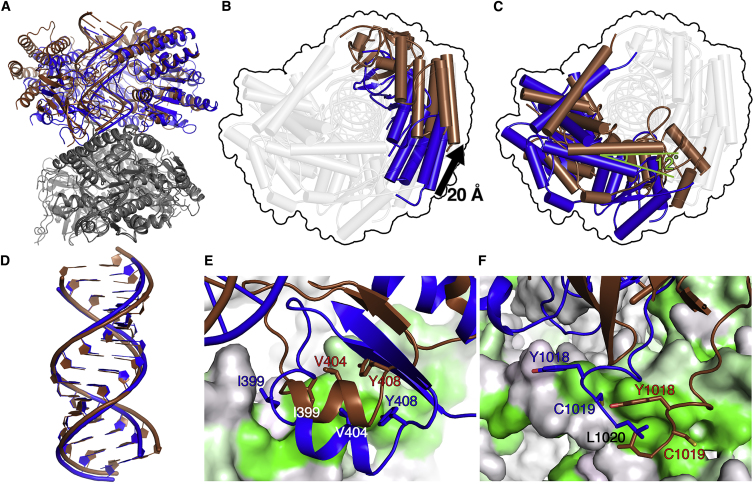
Figure 4.
Differences in Relative Domain Positions and Filament Contacts in the Twist74 and Twist91 Structures
(A) Overview of two protomers of the Twist74 and Twist91 structures superimposed using the pincer domain of the lower protomer (gray) as the reference. The upper protomer of Twist74 is in blue and that of Twist91 is in brown.
(B and C) Top views along the helical axis of the upper protomer from (A) showing the shifts in the positions of Hel2i and CTD (B), and Hel1, Hel2, and pincer (C). The 20 Å translation in Hel2i and 12° rotation in the pincer domain are highlighted. The highlighted domains are colored as in the upper protomer in (A), and the remaining domains are shown in transparent gray for clarity. The outer contour of the superimposed structures is shown for reference as a black outline.
(D) Close-up of the dsRNAs from the Twist74 and Twist91 structures from the structural alignment in (A). The RMSD of the atoms in the 14 superimposed RNA base pairs is 1.23 Å.
(E and F) Close-up views of filament interface I (E) and interface II (F). The protomer of Twist74 shown in gray in (A) and used as the alignment reference is shown in surface representation colored by hydrophobicity as in Figure 2. Key interface residues in the adjacent protomer are shown with Twist74 in blue and Twist91 in brown.