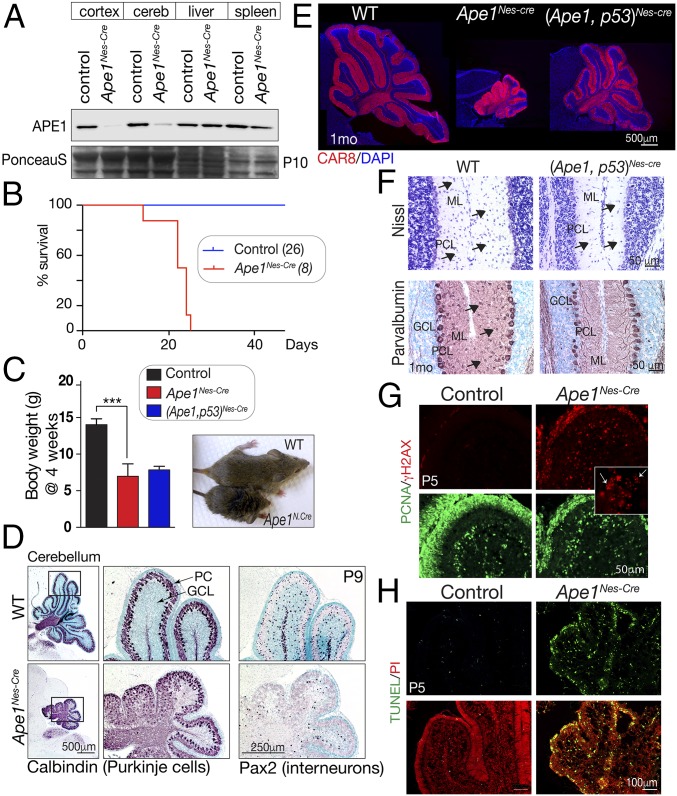
Fig. 1.
Inactivation of APE1 throughout the nervous system. (A) Western blot analysis of various tissues shows that APE1 (∼35 kDa) is deleted in neural tissue (cerebellum and cortex), while normal protein levels are seen in the liver and spleen. Residual APE1 in the Nes-Cre mice is due to blood/lymphocytes, as no protein is detected by immunohistochemistry in perfused tissue. (B) Without intervention, mice with Ape1 deleted in the nervous system (Ape1Nes-cre) survive only to 3 wk of age. (C) Comparative size of control and Ape1Nes-cre animals at 4 wk of age shows the mutants fail to thrive, and substantial weight reduction is apparent. Inactivation of p53 does not rescue this Ape1Nes-cre phenotype. ***P < 0.0002. (D) P9 development of the cerebellum is markedly affected in the Ape1Nes-cre animals, with a disorganization of Purkinje cells (calbindin immunostaining) due to a loss of granule neurons. Interneurons are also lost, as indicated by Pax2 immunostaining. GCL, granule cell layer; PC, Purkinje cells. (E) Mice in which both Ape1 and p53 have been deleted show partial rescue of the cerebellar phenotype. Substantial postnatal cerebellar folia development is found in the (Ape1;p53)Nes-cre tissue, as shown using CAR8 immunostaining to identify Purkinje cells. The WT image is a two-panel composite to allow presentation of the full cerebellum. (F) Interneurons are markedly reduced in the mutant (Ape1;p53)Nes-cre cerebellum, indicating that while loss of p53 rescues a large fraction of granule neurons, stellate and basket interneurons of the molecular layer are not rescued, as indicated by Nissl and parvalbumin staining. GCL, granule cell layer; ML, molecular layer; PC, Purkinje cells. (G) DNA damage is widespread in the developing cerebellum as shown using γH2AX. The Inset shows the typical γH2AX puncta of DNA damage rather than the pan-γH2AX present in apoptotic cells. (H) The loss of granule neurons occurs via apoptosis as the early P5 postnatal cerebellum contains many TUNEL+ cells.