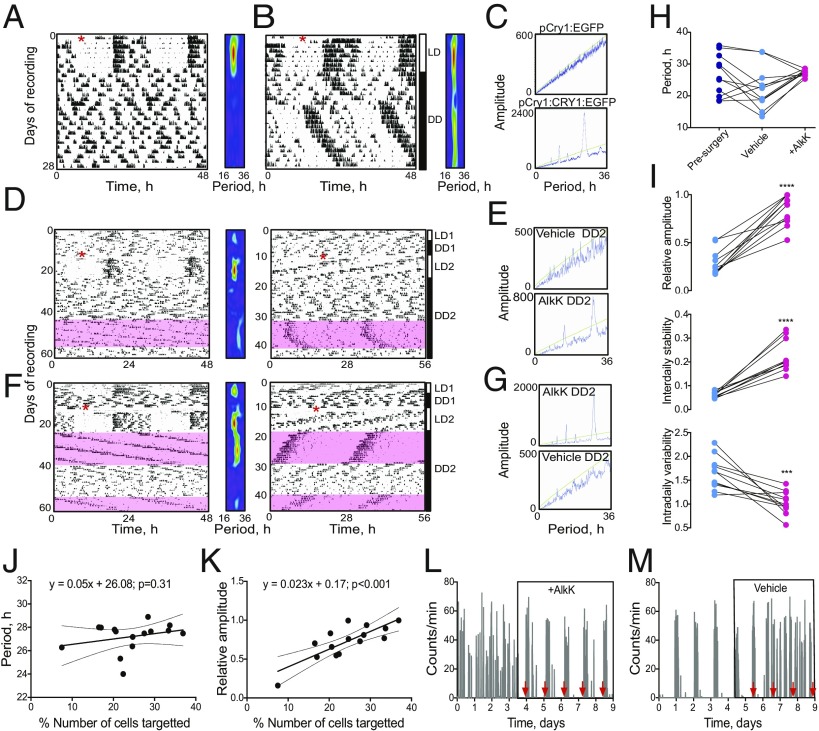
Fig. 4.
Translational switching of Cry1 expression in the SCN controls behavioral circadian rhythms in Cry-null mice. (A and B) Representative double-plotted wheel-running traces and accompanying wavelet analyses from Cry1,2-null mice injected (red asterisks) with control AAV pCry1-EGFP (A) or AAV pCry1-Cry1::EGFP (B) and transferred to DD after 7 d. (C) Periodogram analysis of the DD activity traces shown in A and B reveal the period-appropriate initiation of rhythmicity in the mouse injected with AAV pCry1-Cry1::EGFP. (D) Representative double-plotted actograms and wavelet analysis of arrhythmic Cry1,2-null mouse injected with AAV pCry1-Cry1(177TAG)::EGFP (red asterisk) and transferred to DD after 14 d. Mouse was provided with vehicle drinking water before the switch to 30 mg/mL AlkK (pink shaded area) and then were switched back to vehicle. The data are plotted on a 24-h time base (Left) and a 28-h time base (Right) for ease of inspection. (E) Periodogram analyses for the DD activity traces shown in D during treatment with vehicle or AlkK. (F) Representative actogram as in D, but AlkK (pink-shaded areas) was provided before and after vehicle. Data are plotted on a 24-h time scale (Left) and a 28-h time scale (Right). Corresponding periodogram analyses are shown in G. (H) Estimated circadian periods of activity rhythms of Cry1,2-null mice injected with AAV pCry1-Cry1(177TAG)::EGFP before surgery (navy) and then after surgery during treatment with either vehicle (Veh, light blue) or AlkK (magenta). F(2.20) = 3.6, P < 0.05, one-way repeated-measures ANOVA). (I) Nonparametric measures (relative amplitude, interdaily stability, and intradaily variability) of circadian behavioral rhythms of Cry1,2-null mice injected with AAV pCry1-Cry1(177TAG)::EGFP and then treated with either vehicle (blue) or AlkK (magenta) under DD. ***P < 0.005; ****P < 0.001; paired t test. (J) Linear regression analysis of the percentage of SCN cells expressing the AAV pCry1-Cry1(177TAG)::EGFP against the circadian period observed during treatment with AlkK. (K) As in J, but the relative amplitude of the initiated locomotor activity rhythm during treatment with AlkK is plotted. (L) Representative histogram plot of the activity of Cry1,2-null mouse injected with AAVs and initially on vehicle and then transferred to AlkK. The red arrowheads indicate clear activity onset on days 3–5, and their back-extrapolation for days 1 and 2. (M) As in L, except the transfer was from AlkK to vehicle, and activity onsets are extrapolated forward from the AlkK phase.