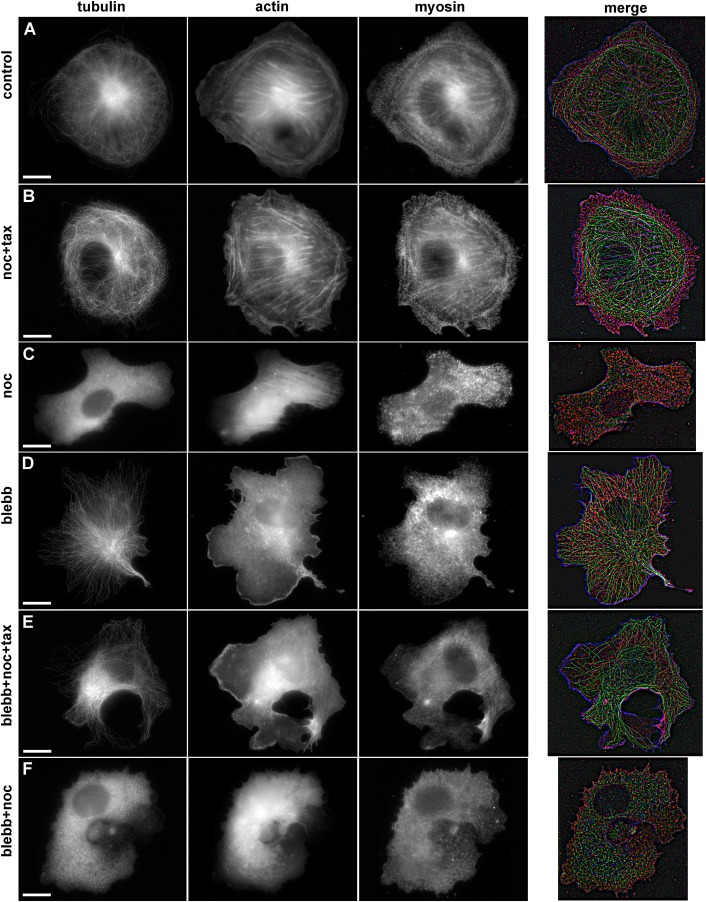
Fig. 5.
Immunofluorescent staining of α-tubulin, actin, and myosin IIa in spreading Vero cells in normal conditions and after treatment with inhibitors. Scale bars: 10 µm. (A) Untreated cell, long MTs form a radial array, with a short distance between their ends and cell margin. Stress fibers are located in the cell body, and diffuse actin staining can be observed in lamellum, myosin II molecules demonstrate periodic banding of actin bundles. (B) Cell with stabilized MTs. MTs are randomly distributed, often buckled, the distance between cell margin and MTs' plus ends is twice more compared to control cells. Long actin fibers stretch across the cell body and small thin actin bundles are present in the lamellum; myosin II demonstrate periodic banding of actin bundles. (C) Cell with depolymerized MTs, tubulin staining is diffuse, thick actin fibers across the cell body, lamellum disappears, myosin II molecules demonstrate periodic banding of actin bundles. (D) Cell treated with blebbistatin. MT array is organized similarly to the control cells, short and thin actin bundles are located in the cell body, myosin is located diffusely in cytoplasm. (E) Cell with stabilized MTs additionally treated with blebbistatin. Randomly distributed MTs do not enter into lamellum, residual short actin bundles are located in the cell body, myosin II is diffusely distributed throughout the cytoplasm. (F) Cell with depolymerized MTs additionally treated with blebbistatin. Residual thin actin bundles are located in the cell body, myosin II is diffusely distributed throughout the cytoplasm.