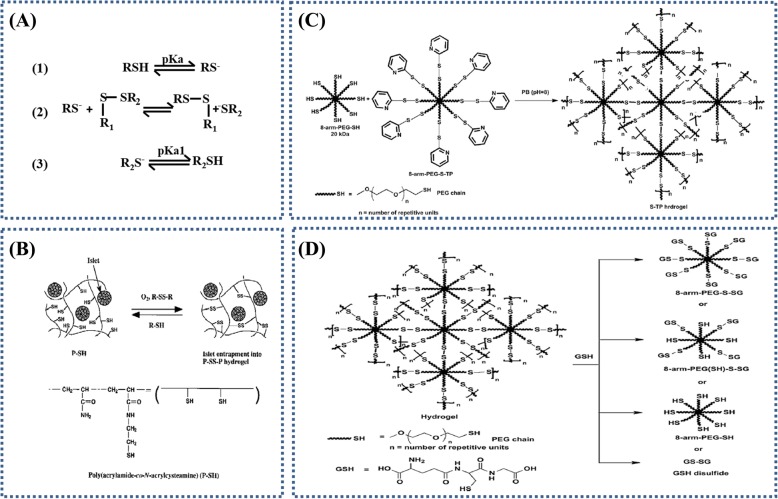
Fig. 3.
Thiol-disulfide exchange reaction based hydrogels formation and theirs dissolution. a Thiol-disulfide exchange reaction. Figure is adapted with permission from the original articles of Houk and Whitesides [43] (Copyright 1987 by Amerian Chemical Society). b Reaction scheme for hydrogel preparation and its reliquefaction. Figure is adapted with permission from the original articles of Hisano et al. [45] (Copyright 1988 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc.). c Schematic representation of thiopyridyl terminations appended on the 8-arm-poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG)-SH to form 8-arm-PEG-S-TP. Thiopyridine is a good leaving group and the 8-arm-PEG-S-TP forms disulfide bridges with the 8-arm-PEG-SH in phosphate buffer (PB) (pH 8) resulting in S-TP hydrogels [47]. d Schematic of the reversible nature of hydrogels. Glutathione (GSH) acts as a thiolate moiety and attacks the disulfide bonds resulting in the breakdown of the hydrogel network (gel to sol transition). The possible products are 8-arm-PEG-SH, 8-arm-PEG-(SH)-S-SG, 8-arm-PEG-S-SG and GS-SG. Figures are adapted with permission from the original articles of Anumolu et al. [47].(Copyright 2010 by Elsevier Ltd.)