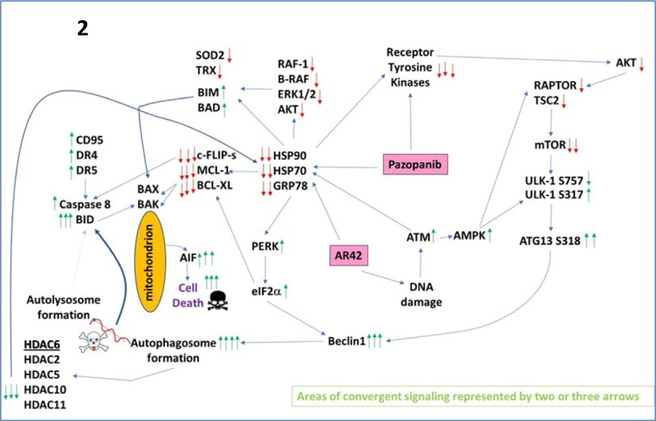
Fig. 2.
A simplified model of the molecular pathways by which pazopanib and AR42 combine to kill cancer cells. As an HDAC inhibitor, AR42 causes DNA damage and causes inhibitory chaperone acetylation. Pazopanib, as a multikinase and chaperone inhibitor, also inhibits chaperone activities as well as many class III receptor tyrosine kinases. DNA damage causes activation of ATM. ATM signals to activate the AMPK. AMPK signaling inactivates RAPTOR and TSC2 resulting in the inactivation of mTORC1 and mTORC2. Downstream of mTOR is the kinase ULK-1; the drug combination via AMPK promotes ULK-1S317 phosphorylation which activates the kinase; the drug combination via mTOR inactivation reduces ULK-1S757 phosphorylation which also activates the kinase. Activated ULK-1 phosphorylates ATG13 which is the key gate-keeper step in permitting autophagosome formation. AR42-induced ATM signaling also acts to reduce the activities of multiple chaperone proteins. Reduced HSP90 and HSP70 function lowers the expression of all receptor tyrosine kinases and the activities of STAT3, STAT5, ERK1/2, and AKT that results in lower expression of ROS/RNS detoxifying enzymes such as TRX and SOD2. Reduced GRP78 function causes activation of PERK and subsequently eIF2α. Enhanced eIF2α signaling reduces the transcription of proteins with short halflives such as c-FLIP-s, MCL-1, and BCL-XL, and enhances expression of Beclin1, DR4, and DR5. Thus, the convergent actions of reduced HSP90 and HSP70 chaperone activity and eIF2α signaling lead to a profound reduction in the protein levels of c-FLIP-s, MCL-1, and BCL-XL which facilitates death receptor signaling through CD95, DR4, and DR5 to activate the extrinsic apoptosis pathway. Enhanced Beclin1 expression converges with elevated ATG13 phosphorylation to produce high levels of autophagosome formation that acts to reduce HDAC2/5/6/10/11 expression but also to stall autophagosome fusion with lysosomes and to stall autolysosome maturation, which likely through cytosolic cathepsin proteases converges with the extrinsic apoptosis pathway to cleave BID and cause mitochondrial dysfunction. Tumor cell killing downstream of the mitochondrion was mediated by AIF and not caspases 3/7. The tumoricidal actions of AIF were facilitated by reduced HSP70 functionality as this chaperone can sequester AIF in the cytosol and prevent its translocation to the nucleus.