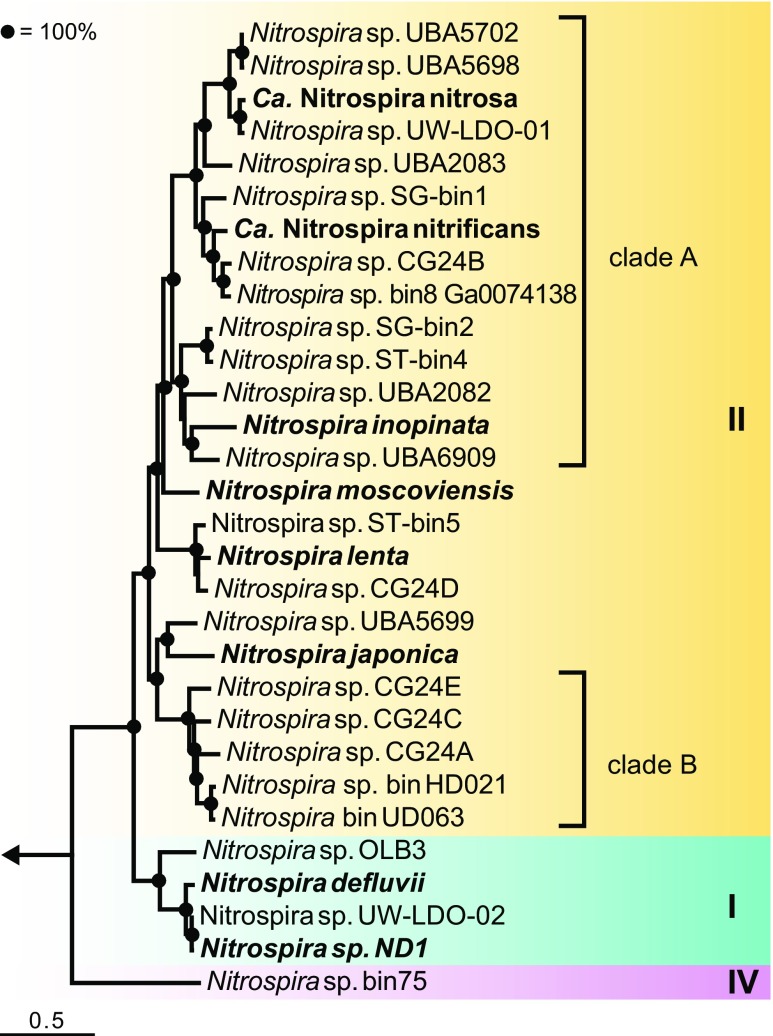
Fig. 1.
Phylogenetic analysis of the genus Nitrospira based on 91 core genes. The UBCG pipeline was used to identify the core gene set consisting of single-copy genes found in most bacterial genomes and for the concatenation of the nucleotide sequence alignments (Na et al. 2018). The tree was reconstructed using RaxML (Stamatakis 2014) on the CIPRES Science Gateway (Miller et al. 2010), using the GTR substitution and GAMMA rate heterogeneity models and 100 bootstrap iterations. Nitrospira lineages are indicated by colored boxes and labeled with roman numerals, comammox clades are designated by square brackets. Two Leptospirillum species were included into the analysis and used for rooting the tree. The position of the outgroup is indicated by the arrow. The scale bar corresponds to 50% estimated sequence divergence. Only genomes with a predicted completeness of > 85% were included in the phylogenetic analysis. For details, see Table S1