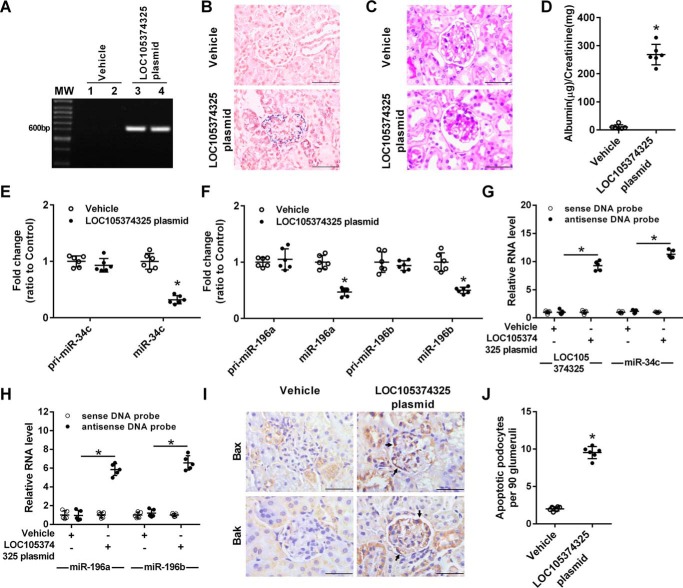
Figure 7.
Effect of exogenous LOC105374325 expression on podocyte injury in mice. A, PCR analysis of LOC105374325 in glomerular tissues of mice treated with control plasmid or LOC105374325-expressing plasmid; B, ISH analysis of LOC105374325 in glomerular tissues of mice (n = 6); C, periodic acid-Schiff staining of renal sections in mice (n = 6); D, urinary albumin excretion in mice (n = 6); E, level of pri-miR-34c and miR-34c in glomerular tissues of mice (n = 6); F, level of pri-miR-196a, miR-196a, pri-miR-196b, and miR-196b in glomerular tissues of mice (n = 6); G and H, RNA pulldown and RT-PCR analysis of the LOC105374325–miR-34c and LOC105374325–miR-196a/b complexes in glomerular tissues of mice (n = 6); I, IHC analysis of Bax and Bak in glomerular tissues of mice (n = 6); J, apoptotic podocytes in glomerular tissues of mice (n = 6). For statistical analysis, a two-tailed Student's t test was used for D, E, F, and J, and one-way ANOVA with Tukey's post hoc test was used for G and H. *, p < 0.05 compared with vehicle control mice. Bar, 20 μm.