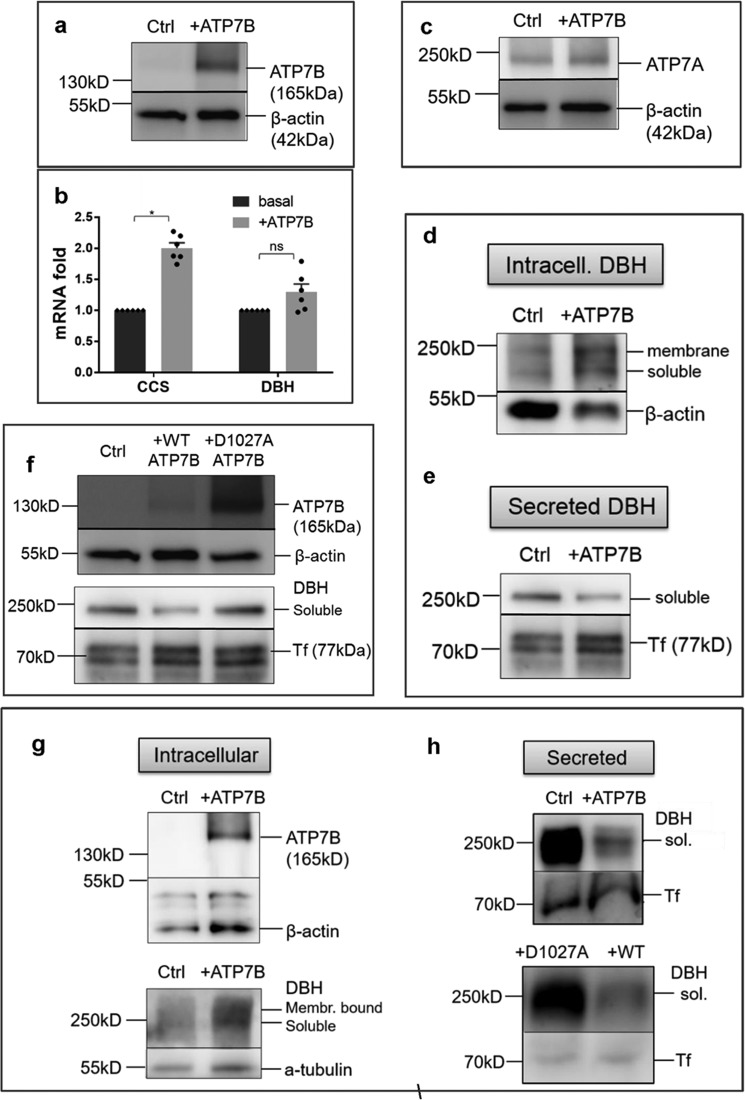
Figure 7.
Overexpression of ATP7B inhibits DBH secretion by lowering Cu in the cytosol. a, ATP7B was overexpressed in SH-SY5Y cells using adenovirus; the endogenous ATP7B in nontransfected controls was barely detectable at the same exposure time. b, ATP7B overexpression is associated with an increase in the CCS mRNA abundance (2.0 ± 0.085-fold, n = 3; p < 0.001) suggestive of the decrease in the cytosolic Cu. DBH mRNA was unchanged (1.3 ± 0.13-fold; p = 0.42). c, ATP7B overexpression does not affect ATP7A abundance. d and e, upon ATP7B overexpression, both soluble and membrane-bound DBH accumulate in cells (d), whereas DBH in the medium is markedly decreased (e). f, top, a catalytically inactive of ATP7B variant (D1027A) is highly expressed compared with WT ATP7B. Bottom, despite higher expression, the D1027A mutant does not decrease the levels of extracellular DBH. g, overexpression of ATP7B in primary cortical neurons (top) is associated with an increased retention of DBH in cells (actin and tubulin are loading controls). h, top, overexpression of WT ATP7B in cortical neurons decreases DBH secretion compared with control. The levels of DBH exported from cells expressing a catalytically inactive D1027A mutant are much higher than from cells expressing the WT ATP7B.