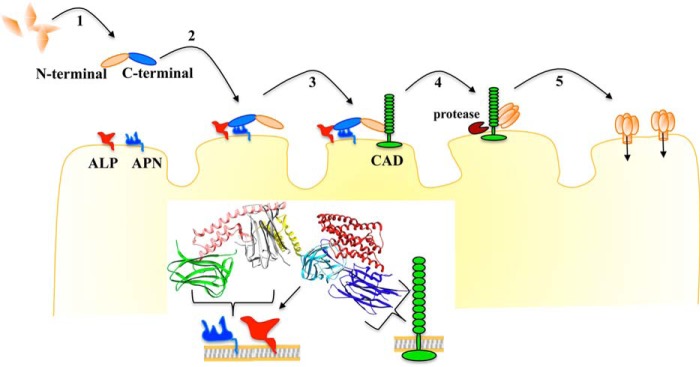
Figure 7.
Proposed mechanism of action of Cry protoxins from Bt. 1, the parasporal crystals are solubilized into protoxin. 2, the C-terminal region of protoxin binds with highly abundant APN and ALP receptors. 3, the protoxin binds to the CAD receptor by the loops of domain II. 4, proteases activate the protoxin, inducing oligomer formation. 5, the oligomer inserts into the membrane, forming a pore that kills the cell. The interaction with APN and ALP with the C-terminal region helps the protoxin to reach the CAD receptor before proteolytic activation, and the interaction of protoxin with CAD in the presence of midgut proteases induces the formation of a robust oligomer that displays high pore formation activity with single conductance and a high open probability, as demonstrated previously (18).