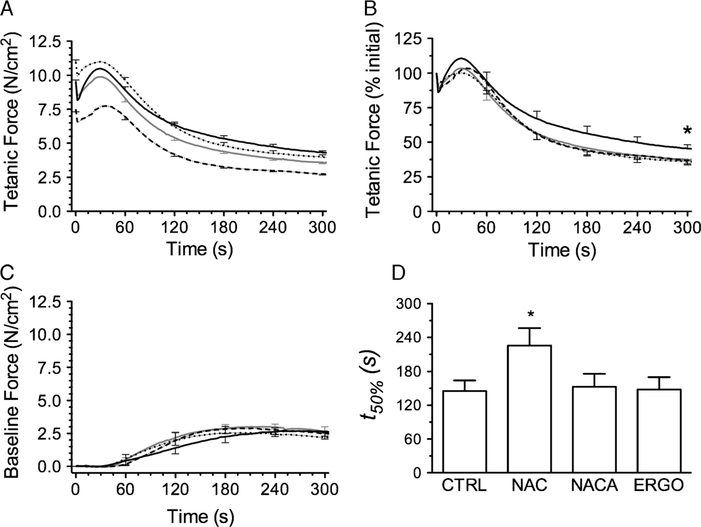
FIGURE 3 —
Temporal changes in tetanic force and baseline tension during fatiguing contractions after exposure to sulfur-based compounds: CTRL (solid gray line), NAC (solid black line), NACA (long-dashed line), ERGO (dotted line). Error bars are shown at 60-s intervals. A, Initial tetanic force was decreased by NACA and increased by ERGO compared with control and NAC (P < 0.05). B, NAC increased tetanic force (%initial) at 300 s compared with CTRL (*P < 0.05). C, Sulfur-based compounds did not affect baseline force throughout the protocol (data from 300 to 600 s not shown). D, Time to reach 50% of initial tetanic force (t50%). *P < 0.05 versus CTRL.