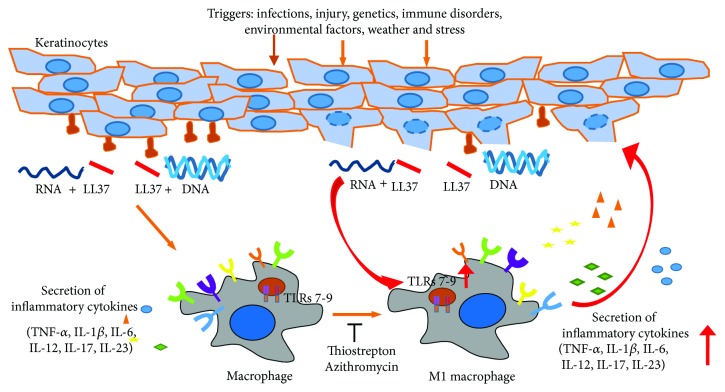
Figure 9.
Model for the role of macrophages in the pathogenic role of Toll-like receptor (TLR) 7- to 9-activated psoriatic inflammation. Ligands of TLRs 7–9 activate cytokine production, TLR 7–9 expression, and M1 polarization in macrophages. M1 macrophages express higher levels of proinflammatory cytokines and TLRs 7–9. These render macrophages to be more inflammatory and further respond to the TLR ligands and lead to an amplification of TLR 7- to 9-activated inflammation at the psoriatic sites. Inhibitors of TLRs 7–9 such as thiostrepton and azithromycin block this TLR-activated M1 macrophage polarization, which can be a mechanism for their inhibitory activity in reducing psoriatic inflammation. Red arrows show the increased expression of TLRs 7–9 and proinflammatory cytokines.