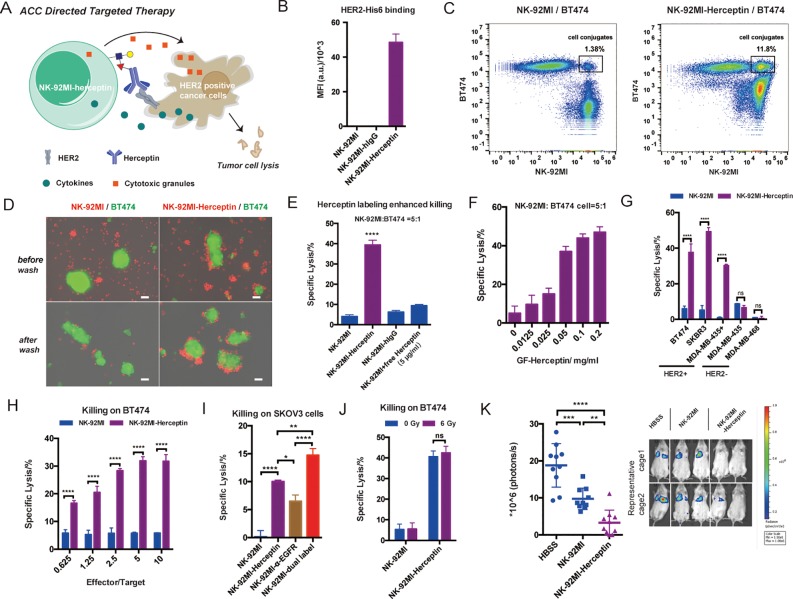
Figure 3.
Construction of Herceptin-NK-92MI conjugates for targeting HER2+ cancer cells: (A) Herceptin-NK-92MI conjugates specifically bind to HER2+ cancer cells and exhibit enhanced killing activities due to proximity effects. (B) Analysis of HER2 binding of Hereceptin-NK-92MI conjugates. Mean ± SD (error bars). Flow cytometry analysis (C) and fluorescent microscopy images (D) of specific binding between Herceptin-NK-92MI conjugates and BT474 (HER2+); NK-92MI cells were stained with CellTracker Orange (red), and BT474 cells were stained with CellTracker Green (green). The merged channels of fluorescence and phase contrast are shown; the green fields represent clusters of BT474 cells. Scale bar: 50 μm. (E) LDH release assay for quantifying induced lysis of BT474 cells by NK-92MI cells; Herceptin-NK-92MI conjugates were compared with parental NK-92MI with or without additionally added free Herceptin (5 μg/mL). hIgG-NK-92MI conjugates were used as a negative control. Mean ± SD (error bars), representative graph from three independent experiments. (F) Killing activity of Herceptin-NK-92MI conjugates constructed at different GF-Herceptin concentrations. Mean ± SD (error bars). (G) Comparisons of NK-92MI and Herceptin-NK-92MI conjugates in killing different cancer cell lines with or without HER2 expression. Mean ± SD (error bars), representative graph from three independent experiments. (H) Comparisons of NK-92MI and Herceptin-NK-92MI conjugates in killing BT474 at different effector-to-target cell ratios. Mean ± SD (error bars). (I) Herceptin and α-EGFR dual-labeled NK-92MI cells were compared with Herceptin-NK-92MI conjugates and α-EGFR-NK-92MI conjugates in killing HER2+EGFR+ SKOV3 cancer cells. Mean ± SD (error bars). (J) Comparison of nonirradiated and irradiated (6 Gy) NK-92MI cells in killing BT474 cells. (K) In vivo antitumor activity of Herceptin-NK-92MI conjugates. NSG mice were injected intravenously with 0.5 million MDA-MB-435/HER2+/F-luc cells. Then, the animals were treated once by IV injection of 3 million NK-92MI or Herceptin-NK-92MI cells on day 1 after the injection of the tumor cells. The control mice received HBSS. Six days after the tumor challenge, the mice were injected IP with d-luciferin and imaged by IVIS system. The sizes of the tumors of the mice and mean values ± SD are shown; n = 10. Representative images also are shown. In all figures, ns, P > 0.05; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001; one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test, two-way ANOVA followed by Sidak’s multiple comparisons test.