Figure 3 |. Key metabolic pathways of the colonic microbiota.
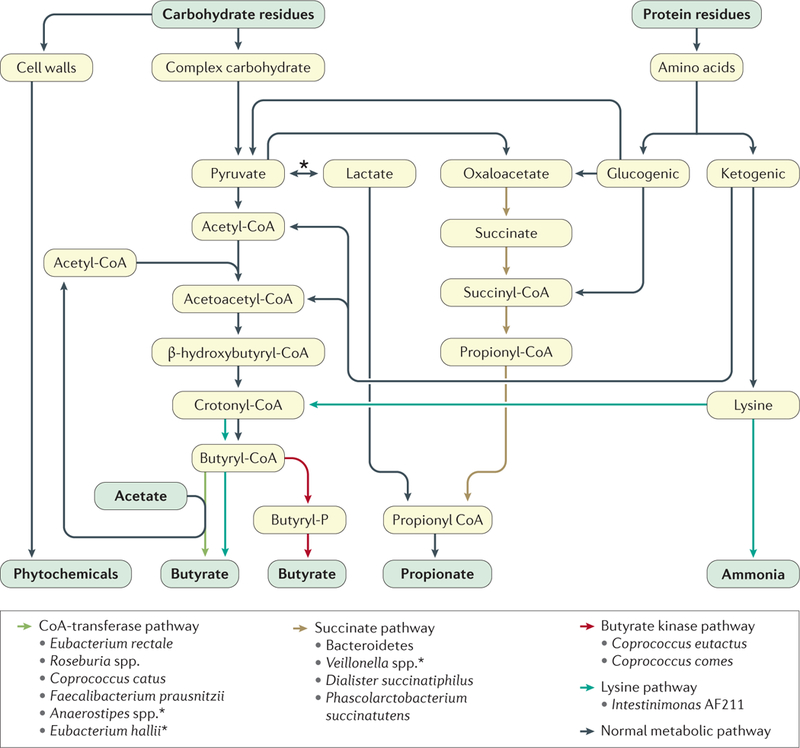
Through the process of fermentation, these metabolic pathways culminate with the production and release of the major short-chain fatty acids (acetate, propionate and butyrate) and phytochemicals from plant cell walls56. Note that there are two microbial enzymes that are responsible for the final synthesis of butyrate, namely butyryl-CoA transferase (dominant, formed by a variety of genera and species) and butyrate kinase (favoured in proteolytic fermentation). Also shown is the pathway for converting the amino acid lysine into butyrate, which also generates ammonia69. The main propionate production pathway is the succinate pathway. Bacterial species found to use certain pathways are shown but are not exhaustive. The asterix indicates species shown to use lactate to form butyrate56.
