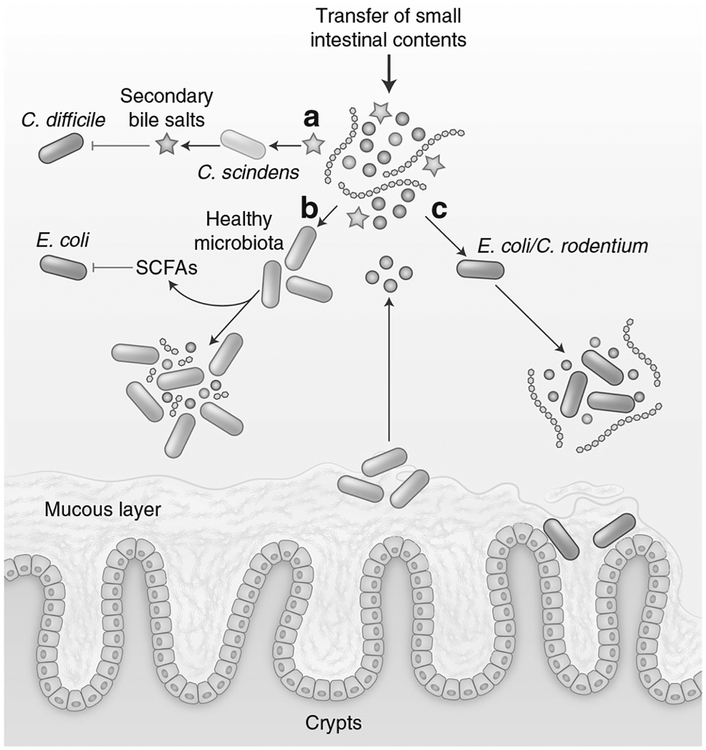
Fig. 1.
Microbiota metabolism contributes to colonization resistance. a Members of the microbiota, such as C. scindens, convert primary bile salts (blue stars) into secondary bile salts (red stars) that inhibit the vegetative growth of C. difficile. b The healthy microbiota ferments diet-derived simple sugars (purple/pink circles), complex polysaccharides (blue lines), and microbiota-liberated metabolites from the mucous layer (brown circles) to produce inhibitory SCFA. c In the absence of competing strains, E. coli and C. rodentium utilize the increased availability of simple sugars for replication