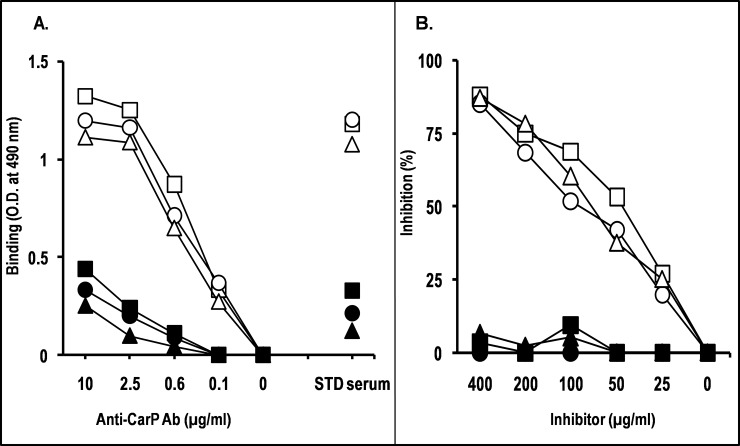
Fig 2. Specificity of anti-CarP Ab assessed by binding and inhibition ELISAs.
(A) In the binding ELISA, microtiter plates were coated with BSA (square), HA (circle), or FIB (triangle), in carbamylated form (empty symbols) or native form (filled symbols). Wells were incubated PBS containing serial dilutions of anti-CarP Ab. Standard (STD) serum was used as specificity control. Bound IgG was revealed with HRP-conjugated anti-human IgG and o-phenylenediamine. The data are representative of at least two independent experiments. (B) In the inhibition assay, anti-CarP Ab were diluted in PBS-BSA to the lowest concentration giving 80%–100% of maximal A490 in the binding assay (2.5 μg/ml), and pre-incubated with an equal volume of PBS containing 2-fold serial dilutions of BSA (square), HA (circle), or FIB (triangle), in carbamylated form (empty symbols) or native form (filled symbols). Following a 2-h incubation at room temperature, the mixture was added to microtiter plate wells coated with CarBSA. After a 4-h incubation at room temperature and three washes, bound IgG was detected with HRP-conjugated anti-human IgG (Fc portion) and o-phenylenediamine. Results are expressed as percentage of binding inhibition compared with binding in the absence of inhibitor. The data are representative of at least two independent experiments.