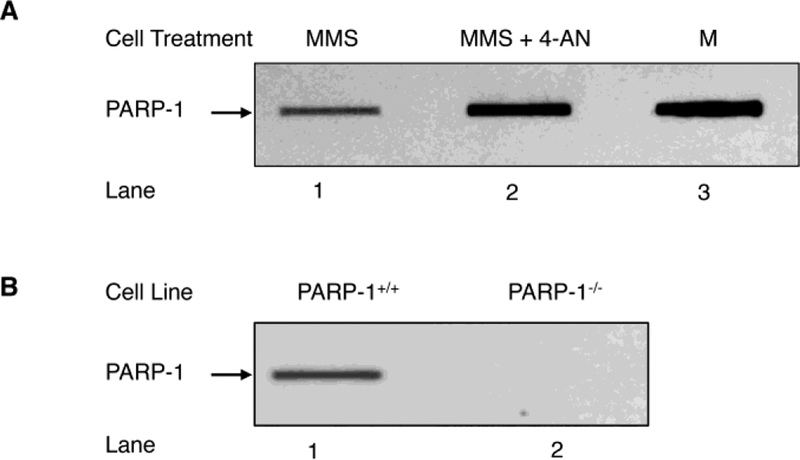
Fig. 1.
Detection of PARP-1 DPCs in genomic DNA by the RADAR method. (A) PARP-1 DPCs are formed as a function of AP sites in the genomic DNA. PARP-1+/+ MEFs were treated with MMS (lane 1) or MMS plus 4-AN (lane 2), as described under “Materials and Methods”. An equal amount of the genomic DNA (5 μg) isolated from PARP-1+/+ cells treated with MMS or with MMS plus 4-AN was applied into slot blot wells, as indicated. The blot was probed with anti-PARP-1 antibody. Lane 3, represents a sample of purified PARP-1 used as a positive control (M). (B) Requirement of PARP-1 expression for detection of PARP-1 DPC formation in cells. Genomic DNA (5 μg) from MMS treated PARP-1+/+ (lane 1) or PARP-1−/− (lane 2) MEFs was used for slot blot analysis as in (A). PARP-1−/− cells failed to show PARP-1 DPCs (lane 2), indicating PARP-1 DPC is specific to expression of PARP-1. The results shown are representative of at least three independent experiments.