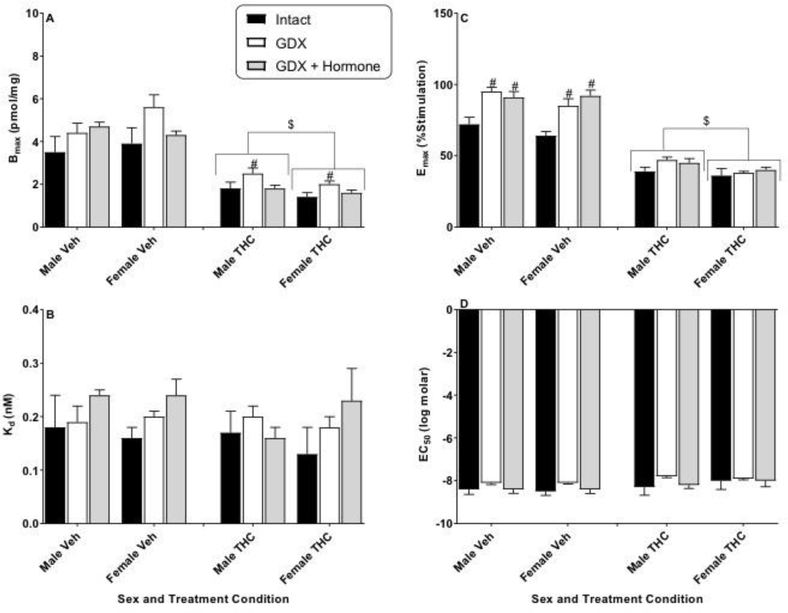
Figure 2.
Effects of sex and hormonal status on [3H]SR141761A saturation binding (Bmax and Kd) and CP55,940-stimulated [35S]GTPγS binding (Emax and EC50) in the prefrontal cortex of vehicle- (Veh) or THC-treated adult rats of both sexes. Rats were gonadally intact (i.e., sham gonadectomy) (filled black bars) or had undergone gonadectomy (GDX) with or without hormone replacement (filled grey bars and unfilled bars, respectively). Each point represents the mean (± SEM) of data for 4 rats in each condition. Based upon curves fitted to the binding values, four dependent measures were calculated: Bmax (panel A), Kd (panel B), Emax (panel C), and EC50 (panel D). Three-way ANOVA showed significant THC-induced decreases in Bmax and Emax for prefrontal cortex (vs. Veh). For 2-way (sex X hormonal status) ANOVAs: $ p<0.05, main effect of sex for designated measure (i.e., different between sexes when collapsed across hormonal condition). # p<0.05, main effect of hormonal condition compared to intact (i.e., hormonal condition produced different results vs intact when collapsed across sex).