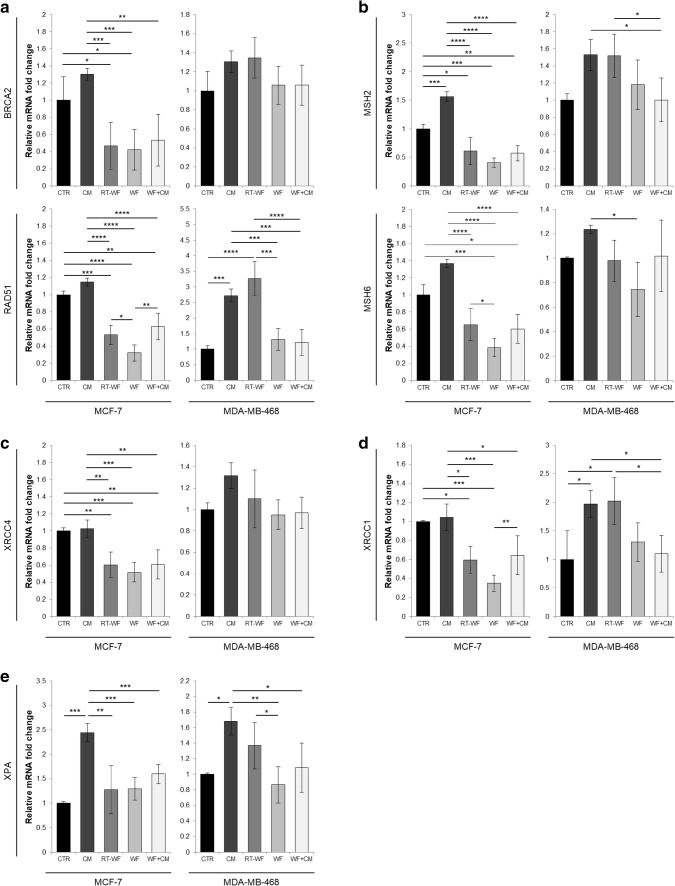
Fig. 4.
IORT modifies the effect of wound fluids on the activation of the DNA damage repair-related pathways in the breast cancer cells, marked by the up-regulation of the DNA repair-related genes. RT-qPCR was used to measure the expression of chosen DNA damage repair pathway genes: a homologous recombination (genes: RAD51, BRCA2), b mismatch repair (genes: MSH2, MSH6), c non-homologous end joining (gene: XRCC4), d base excision repair (gene: XRCC1), e nucleotide excision repair (gene: XPA). Data are presented as histograms compiled from samples representative of each group and as means ± standard deviation, normalized to the untreated controls. N = at least 3 independent biological replicates. CM conditioned medium collected from irradiated breast cancer cells, RT-WF wound fluid collected 48 h after surgical excision of the tumour followed by IORT treatment, WF wound fluid collected 48 h after surgical excision of the tumour, WF + CM combination of equal volumes of wound fluid collected after surgical excision of the tumour with conditioned medium from irradiated breast cancer cells. Results were considered statistically significant at *p < 0.05; **p ≤ 0.01; ***p ≤ 0.001; ****p ≤ 0.0001